Dangerous Climate Whiplash: Global Cities Face Impacts, Report Reveals

Table of Contents
Increased Frequency and Intensity of Extreme Weather Events
The report highlights a dramatic increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, directly linked to climate change. This dangerous climate whiplash manifests in several devastating ways for urban areas.
Heatwaves and Their Urban Impact: The urban heat island effect, where cities retain more heat than surrounding areas, exacerbates the impact of heatwaves. This leads to:
- Increased mortality rates: Heatstroke and other heat-related illnesses are significantly increasing, placing a strain on healthcare systems.
- Strain on healthcare systems: Hospitals and emergency services are overwhelmed during extreme heat events, leading to delays in care.
- Reduced worker productivity: High temperatures reduce worker efficiency and increase workplace accidents.
- Damage to infrastructure: Extreme heat can cause damage to roads, bridges, and power grids.
Cities like Phoenix, Arizona, and London, England, have experienced record-breaking heatwaves in recent years, showcasing the devastating consequences of this aspect of dangerous climate whiplash.
Flooding and its Devastating Consequences: Intense rainfall and rising sea levels are increasing the risk of flash floods and coastal inundation. The consequences are severe:
- Damage to property and infrastructure: Flooding causes extensive damage to homes, businesses, and vital infrastructure, leading to massive economic losses.
- Displacement of populations: Many people are forced to evacuate their homes due to flooding, leading to displacement and social disruption.
- Disruption of essential services: Flooding can disrupt transportation, power, water, and sanitation services, impacting daily life.
- Economic losses: The costs associated with flood damage, recovery, and displacement are substantial, impacting local and national economies.
Cities like Jakarta, Indonesia, and New Orleans, Louisiana, are prime examples of cities battling devastating floods, highlighting the vulnerability of coastal megacities to dangerous climate whiplash.
The Impact of Droughts and Water Scarcity: Prolonged droughts are stressing urban water supplies, especially in rapidly growing cities with limited water resources. This leads to:
- Water restrictions: Cities implement water rationing and usage limitations, impacting residents and businesses.
- Agricultural impacts: Droughts reduce agricultural yields, impacting food security and local economies.
- Increased risk of wildfires: Dry conditions increase the risk of wildfires, endangering lives and property.
- Potential for social unrest: Competition for scarce water resources can exacerbate social inequalities and lead to conflict.
Cape Town, South Africa, faced a severe water crisis in recent years, showcasing the extreme risks of drought in urban environments, illustrating a critical dimension of dangerous climate whiplash.
Vulnerability of Urban Infrastructure and Populations
Aging Infrastructure and Climate Resilience: Many cities possess aging infrastructure ill-equipped to handle the increased intensity of extreme weather events. This includes:
- Inadequate drainage systems: Existing drainage systems are often insufficient to cope with intense rainfall, leading to flooding.
- Insufficient flood defenses: Many cities lack adequate flood defenses to protect against rising sea levels and storm surges.
- Vulnerability of power grids: Extreme weather can damage power lines and substations, leading to widespread power outages.
- Outdated building codes: Older buildings may not meet modern standards for climate resilience, increasing vulnerability to damage.
Social Inequality and Climate Impacts: Marginalized communities often bear the brunt of climate change impacts due to:
- Higher mortality rates among vulnerable populations: Poor and marginalized communities often lack access to resources and support during extreme weather events.
- Increased displacement: Vulnerable populations are often more likely to be displaced by extreme weather events due to inadequate housing and limited resources.
- Exacerbation of existing social inequalities: Climate change impacts can exacerbate existing inequalities, widening the gap between the rich and the poor.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Cities
Addressing dangerous climate whiplash requires proactive strategies focusing on mitigation and adaptation.
Investing in Climate-Resilient Infrastructure: Cities must invest in robust infrastructure capable of withstanding extreme weather:
- Upgrading drainage systems: Improved drainage systems can help prevent flooding during intense rainfall.
- Building seawalls: Seawalls and other coastal defenses can protect against rising sea levels and storm surges.
- Improving building codes: Stricter building codes can ensure that new buildings are more resilient to extreme weather.
- Investing in renewable energy sources: Transitioning to renewable energy can reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions.
Implementing Effective Early Warning Systems: Early warning systems are crucial for mitigating the impact of extreme weather events:
- Improved weather forecasting: Accurate and timely weather forecasts can provide advance warning of impending extreme weather.
- Public awareness campaigns: Public education campaigns can help residents prepare for extreme weather events.
- Emergency response plans: Well-developed emergency response plans can help minimize casualties and damage during extreme weather.
- Community preparedness initiatives: Community-based initiatives can help build resilience and prepare for extreme weather events.
Promoting Sustainable Urban Planning: Sustainable urban planning practices are essential for reducing urban vulnerability:
- Green infrastructure: Green spaces can help mitigate the urban heat island effect and reduce flooding.
- Urban forestry: Trees can help absorb rainwater and reduce the impact of heatwaves.
- Improved water management: Efficient water management strategies can help ensure access to water during droughts.
- Sustainable transportation systems: Sustainable transportation systems can reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Conclusion
The report's findings clearly demonstrate the severe impacts of dangerous climate whiplash on global cities. The increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, coupled with vulnerable infrastructure and social inequalities, pose a significant threat to urban populations worldwide. Addressing dangerous climate whiplash requires immediate and collaborative action. Global cities must prioritize investments in climate-resilient infrastructure, implement effective early warning systems, and adopt sustainable urban planning practices to protect their citizens and secure their future. Failure to act decisively will only exacerbate the long-term consequences of climate change, leading to greater instability and suffering. The time for decisive action to combat dangerous climate whiplash is now.

Featured Posts
-
 Nba Playoffs Mathurin And Hunter Involved In Game 4 Ejection
May 28, 2025
Nba Playoffs Mathurin And Hunter Involved In Game 4 Ejection
May 28, 2025 -
 Seriozno E Khyu Dzhakman I Stn Fostr Zaedno
May 28, 2025
Seriozno E Khyu Dzhakman I Stn Fostr Zaedno
May 28, 2025 -
 Meilleur Prix Samsung Galaxy S25 512 Go 985 56 E
May 28, 2025
Meilleur Prix Samsung Galaxy S25 512 Go 985 56 E
May 28, 2025 -
 Tough Road Ahead Sinners French Open Draw Analysis
May 28, 2025
Tough Road Ahead Sinners French Open Draw Analysis
May 28, 2025 -
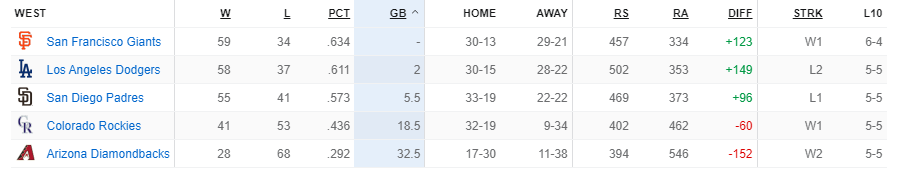 Nl West Standings Shake Up Arraez Injured Dodgers On Fire Diamondbacks Closing In
May 28, 2025
Nl West Standings Shake Up Arraez Injured Dodgers On Fire Diamondbacks Closing In
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Rbcs Earnings And The Rising Tide Of Bad Loans What Investors Need To Know
May 31, 2025
Rbcs Earnings And The Rising Tide Of Bad Loans What Investors Need To Know
May 31, 2025 -
 Addressing The Housing Crisis The Importance Of Provincial Action
May 31, 2025
Addressing The Housing Crisis The Importance Of Provincial Action
May 31, 2025 -
 Donate And Bid 2025 Love Moto Stop Cancer Online Auction
May 31, 2025
Donate And Bid 2025 Love Moto Stop Cancer Online Auction
May 31, 2025 -
 The Impact Of Souring Loans On Rbcs Latest Earnings Report
May 31, 2025
The Impact Of Souring Loans On Rbcs Latest Earnings Report
May 31, 2025 -
 The 2025 Love Moto Stop Cancer Online Auction Is Open
May 31, 2025
The 2025 Love Moto Stop Cancer Online Auction Is Open
May 31, 2025
