Higher Inflation And Unemployment: Fueling Economic Uncertainty
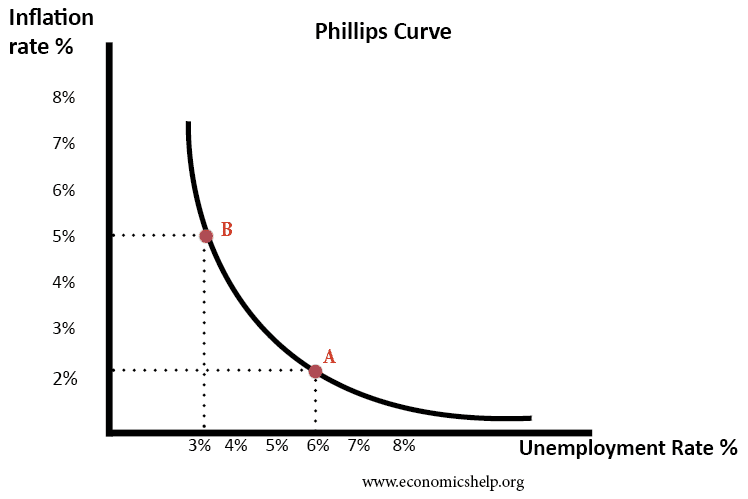
Table of Contents
The Inflationary Spiral: Understanding Rising Prices
Inflation, simply put, is a general increase in prices across an economy. This can manifest in several ways, including demand-pull inflation (driven by excess demand) and cost-push inflation (driven by rising production costs). Currently, we're witnessing a complex interplay of both. The impact of inflation on purchasing power is significant; as prices rise, the same amount of money buys fewer goods and services, reducing consumer spending.
Several factors are contributing to the current high inflation rates:
- Rising energy prices: The global energy market remains volatile, with significant price increases impacting transportation, manufacturing, and household budgets.
- Supply chain bottlenecks: Disruptions to global supply chains, exacerbated by geopolitical events and the lingering effects of the pandemic, continue to constrain the availability of goods and drive up prices.
- Increased demand: Post-pandemic economic recovery has led to increased consumer demand, further contributing to upward pressure on prices.
- Impact on consumer goods: The cost of everyday necessities, from food to housing, has increased significantly, squeezing household budgets and reducing disposable income.
- Impact on businesses: Businesses face rising input costs, forcing them to either absorb losses or pass increased prices onto consumers, potentially triggering a wage-price spiral.
Unemployment's Upward Trend: A Deeper Dive into Job Losses
Unemployment represents a significant economic and social challenge. Types of unemployment include frictional (temporary unemployment between jobs), cyclical (related to economic downturns), and structural (due to mismatches between skills and available jobs). High unemployment leads to reduced consumer spending, increased social welfare costs, and a decrease in overall economic output.
Contributing factors to current high unemployment rates include:
- Job losses in specific sectors: Certain industries, particularly those sensitive to economic downturns, have experienced significant job losses.
- Rising cost of living impact on unemployment: High inflation erodes real wages, making it harder for individuals to maintain their standard of living, potentially leading to job losses or reduced hours.
- Impact on national GDP: High unemployment directly translates to a lower Gross Domestic Product (GDP), indicating a less productive economy.
- Government response to unemployment: Government policies and programs aimed at addressing unemployment play a vital role in mitigating the impact of job losses.
The Interplay of Inflation and Unemployment: A Vicious Cycle
The Phillips Curve traditionally suggests an inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment – low unemployment correlates with high inflation, and vice versa. However, the current economic climate challenges this simple model. High inflation can lead to higher unemployment through reduced investment, decreased consumer spending, and potential economic slowdowns. Conversely, high unemployment can fuel deflationary pressures, which can then trigger further economic contraction and job losses. Stagflation, a period of simultaneous high inflation and high unemployment, represents a particularly challenging scenario. Policymakers face a difficult task in addressing both issues concurrently, as policies aimed at curbing inflation might exacerbate unemployment, and vice versa.
- Wage-price spiral: High inflation can lead to demands for higher wages, which in turn can push prices even higher, creating a self-reinforcing cycle.
- Reduced investment: Economic uncertainty discourages businesses from investing in expansion and job creation.
- Impact on economic growth: The combined effect of high inflation and unemployment significantly hinders economic growth.
- Government policy responses: Governments must carefully calibrate monetary and fiscal policies to address both inflation and unemployment without exacerbating either problem.
Economic Uncertainty and its Ripple Effects: Assessing the Risks
Higher inflation and unemployment create significant economic uncertainty for businesses, consumers, and investors. This uncertainty leads to:
- Reduced consumer confidence: Consumers are less likely to spend when faced with high prices and job insecurity.
- Decreased investment in new projects: Businesses postpone investments due to uncertainty about future demand and profitability.
- Increased risk aversion: Investors become more cautious, seeking safer assets and reducing investment in riskier ventures.
- Volatility in financial markets: Uncertainty can lead to increased volatility in stock markets and other financial assets.
- Impact on global economy: The interconnected nature of the global economy means that economic problems in one region can quickly spread to others.
Mitigating the Impact of Higher Inflation and Unemployment: A Path Forward
The interconnected nature of higher inflation and unemployment presents significant challenges to policymakers. Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach that includes monetary policy adjustments (such as interest rate changes), fiscal stimulus (such as government spending programs), and structural reforms aimed at boosting productivity and efficiency. Understanding the complexities of higher inflation and unemployment is crucial for navigating these uncertain economic times. Stay informed and engage in discussions to help shape policies that mitigate the impact of higher inflation and unemployment on our economy.

Featured Posts
-
 Jungkooks Plans And Btss Future Addressing 10 Popular Queries
May 30, 2025
Jungkooks Plans And Btss Future Addressing 10 Popular Queries
May 30, 2025 -
 Live Stock Market Updates Dow Jones S And P 500 And Nasdaq May 29
May 30, 2025
Live Stock Market Updates Dow Jones S And P 500 And Nasdaq May 29
May 30, 2025 -
 Jones Vs Aspinall Heated Exchange Highlights Ufc Rivalry
May 30, 2025
Jones Vs Aspinall Heated Exchange Highlights Ufc Rivalry
May 30, 2025 -
 Tileoptikes Metadoseis Tetartis 23 Aprilioy Odigos Programmatos
May 30, 2025
Tileoptikes Metadoseis Tetartis 23 Aprilioy Odigos Programmatos
May 30, 2025 -
 Setlist Fm Y Ticketmaster Una Alianza Para La Compra De Boletos
May 30, 2025
Setlist Fm Y Ticketmaster Una Alianza Para La Compra De Boletos
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Factors Behind Thompsons Monte Carlo Failure
May 31, 2025
The Factors Behind Thompsons Monte Carlo Failure
May 31, 2025 -
 New Covid 19 Variant What We Know About The Recent Case Surge
May 31, 2025
New Covid 19 Variant What We Know About The Recent Case Surge
May 31, 2025 -
 A Look At Thompsons Losses In Monte Carlo
May 31, 2025
A Look At Thompsons Losses In Monte Carlo
May 31, 2025 -
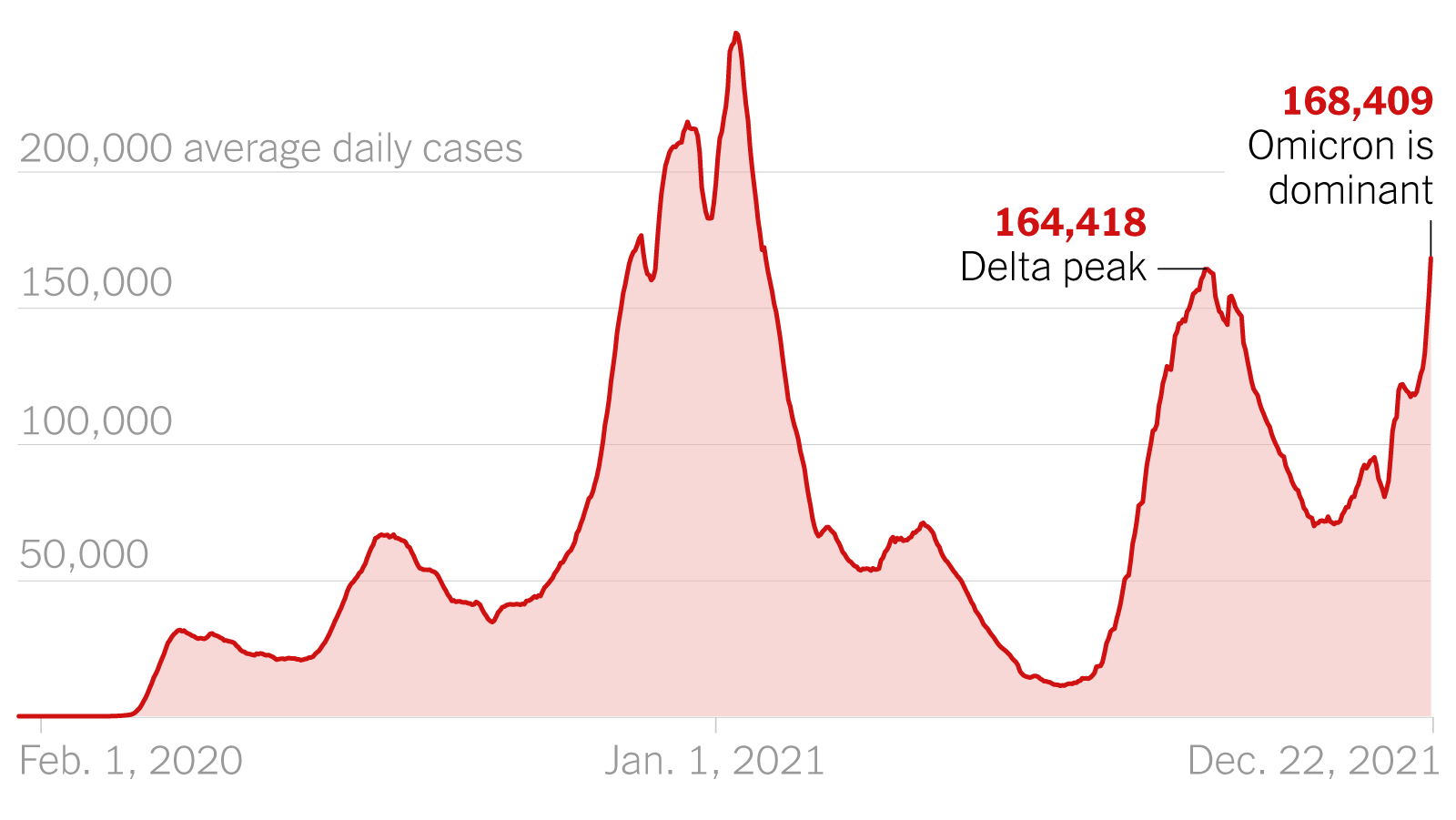 Analysis The Link Between A New Covid 19 Variant And Increased Infections
May 31, 2025
Analysis The Link Between A New Covid 19 Variant And Increased Infections
May 31, 2025 -
 Thompsons Monte Carlo Challenges A Comprehensive Review
May 31, 2025
Thompsons Monte Carlo Challenges A Comprehensive Review
May 31, 2025
