Japan's Economic Performance Q1: Shrinking Before US Tariffs

Table of Contents
Key Factors Contributing to Japan's Q1 Economic Contraction
Several interconnected factors contributed to the disappointing Q1 figures for Japan's economic performance. Analyzing these factors is crucial to understanding the current state and predicting future trends in the Japanese economy.
Weakening Domestic Demand
A significant contributor to the contraction was weakening domestic demand. This was characterized by a decrease in both consumer spending and business investment.
- Reduced consumer confidence: Following the October 2023 consumption tax hike, consumer confidence plummeted, leading to decreased spending on durable goods and discretionary items. This is reflected in [cite specific data source, e.g., the Consumer Confidence Index].
- Impact of the consumption tax hike: The increase in consumption tax dampened consumer spending, as predicted by many economists. The negative impact on Japan's economic performance was more pronounced than initially forecast.
- Decreased business investment due to uncertainty: Uncertainty surrounding global trade and the potential for further US tariffs led to a decline in business investment. Companies delayed expansion plans, opting for a wait-and-see approach.
Impact of Global Economic Slowdown
The slowdown in global economic growth significantly impacted Japan's export-oriented economy. Reduced demand from key trading partners, particularly China and the US, exacerbated the contraction.
- Declining exports in key sectors (automobiles, electronics): Exports of automobiles and electronics, two key pillars of the Japanese economy, experienced significant declines. This is partly attributed to weakening global demand and trade disputes. [Cite data source for export figures].
- Weakening global supply chains: Disruptions to global supply chains, stemming from geopolitical uncertainties and trade wars, further hampered Japan's export performance. Companies faced difficulties sourcing components and delivering finished goods.
- Uncertainty surrounding Brexit and other geopolitical factors: Ongoing uncertainty surrounding Brexit and other geopolitical events created a climate of economic instability, impacting investor confidence and business decisions.
Natural Disasters and Their Economic Fallout
Several natural disasters, including powerful typhoons, struck Japan during Q1, resulting in significant economic disruption.
- Disruptions to supply chains: Typhoons caused widespread damage to infrastructure, disrupting supply chains and impacting production across various sectors. This led to delays in shipments and increased production costs.
- Damage to agricultural output: Agricultural production was severely impacted by the typhoons, leading to shortages of certain goods and driving up food prices.
- Increased insurance claims and reconstruction costs: The aftermath of the natural disasters resulted in substantial insurance claims and increased government spending on reconstruction efforts, putting further strain on the Japanese economy.
The Looming Threat of US Tariffs on Japan's Economy
The potential for increased US tariffs on Japanese goods poses a significant threat to Japan's economic performance. This threat adds another layer of complexity to the already challenging economic climate.
Potential Sectors Affected
Several key sectors of the Japanese economy are particularly vulnerable to increased US tariffs.
- Increased prices for Japanese goods in the US market: Higher tariffs would increase the prices of Japanese goods in the US, reducing their competitiveness and potentially leading to decreased demand.
- Reduced competitiveness against other exporting nations: Increased tariffs would make Japanese goods more expensive compared to those from other countries, potentially leading to a loss of market share.
- Potential job losses in export-oriented industries: If demand for Japanese goods falls significantly, it could lead to job losses in export-oriented industries, further impacting Japan's economic performance.
Government Response and Mitigation Strategies
The Japanese government has implemented various measures to address the economic contraction and mitigate the potential impact of US tariffs.
- Fiscal stimulus measures: The government has announced fiscal stimulus packages aimed at boosting domestic demand and supporting businesses. [Detail specific measures].
- Monetary policy adjustments: The Bank of Japan may adjust monetary policy to stimulate economic activity. [Describe potential policy changes].
- Trade negotiations with the US: The Japanese government is engaging in trade negotiations with the US to reach a mutually beneficial agreement and avoid escalating trade tensions.
Long-Term Implications for Japan's Economic Growth
The Q1 contraction, coupled with the threat of US tariffs, has significant long-term implications for Japan's economic growth.
- Impact on foreign investment: Uncertainty surrounding the economic outlook and trade policies could negatively impact foreign investment in Japan.
- Long-term implications for employment: Sustained economic weakness could lead to long-term unemployment issues.
- Potential for economic stagnation or recovery: The future trajectory of Japan's economic performance hinges on the effectiveness of government policies, the resolution of trade disputes, and the strength of global economic growth. Structural reforms, such as increased productivity and investment in innovation, are essential for long-term economic recovery.
Conclusion
Japan's Q1 economic contraction highlights the vulnerability of the Japanese economy to both domestic and global factors. The potential impact of increased US tariffs adds further uncertainty to the outlook. Understanding the interplay of these factors, including weakening domestic demand, a global economic slowdown, the impact of natural disasters, and the threat of US tariffs, is crucial for predicting future economic performance.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the latest developments in Japan's economic performance and the ongoing US-Japan trade negotiations. Regularly monitor updates on Japan's economic indicators to better understand the evolving situation and its implications for businesses and investors. Further research into Japan's economic performance is vital to navigating this complex economic landscape.

Featured Posts
-
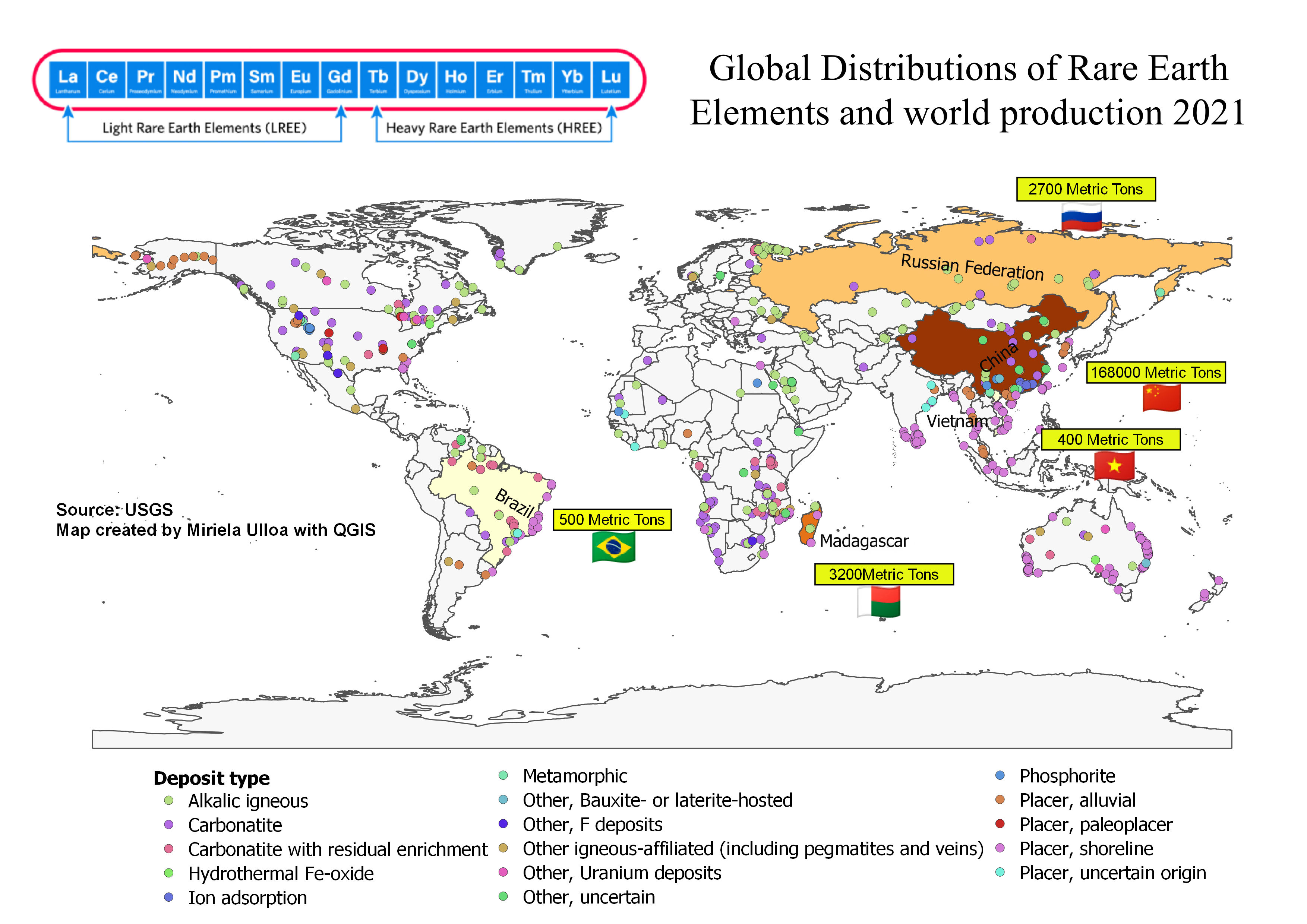 Global Heavy Rare Earths Market Lynass Rise As A Major Player
May 17, 2025
Global Heavy Rare Earths Market Lynass Rise As A Major Player
May 17, 2025 -
 Tam Krwz Ke Jwtwn Pr Pawn Rkhne Waly Khatwn Mdah Awr Adakar Ka Rdeml
May 17, 2025
Tam Krwz Ke Jwtwn Pr Pawn Rkhne Waly Khatwn Mdah Awr Adakar Ka Rdeml
May 17, 2025 -
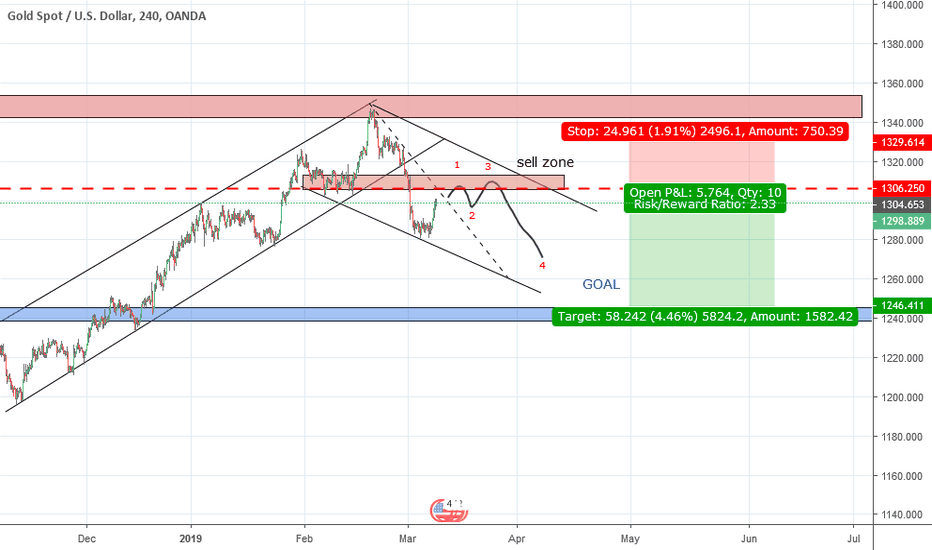 Xauusd Gold Price Recovery Us Economic Data And Interest Rate Outlook
May 17, 2025
Xauusd Gold Price Recovery Us Economic Data And Interest Rate Outlook
May 17, 2025 -
 Noise Reduction In Tokyo Apartments A Guide To Soundproof Living
May 17, 2025
Noise Reduction In Tokyo Apartments A Guide To Soundproof Living
May 17, 2025 -
 Luxury And Tranquility Soundproof Apartments And Salons In Tokyos Real Estate Market
May 17, 2025
Luxury And Tranquility Soundproof Apartments And Salons In Tokyos Real Estate Market
May 17, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Millions Made From Exec Office365 Hacks Fbi Investigation Reveals
May 17, 2025
Millions Made From Exec Office365 Hacks Fbi Investigation Reveals
May 17, 2025 -
 T Mobile To Pay 16 Million For Data Breaches Over Three Year Period
May 17, 2025
T Mobile To Pay 16 Million For Data Breaches Over Three Year Period
May 17, 2025 -
 16 Million Penalty For T Mobile A Three Year Data Breach Investigation
May 17, 2025
16 Million Penalty For T Mobile A Three Year Data Breach Investigation
May 17, 2025 -
 Is Creatine Safe And Effective A Comprehensive Review
May 17, 2025
Is Creatine Safe And Effective A Comprehensive Review
May 17, 2025 -
 Creatine 101 Your Guide To Understanding And Using Creatine
May 17, 2025
Creatine 101 Your Guide To Understanding And Using Creatine
May 17, 2025
