New US Energy Policy: Will Consumers Face Higher Prices?

Table of Contents
Keywords: New US energy policy, energy prices, electricity prices, gas prices, consumer energy costs, clean energy transition, energy policy impact, inflation, renewable energy, fossil fuels.
The recently implemented US energy policy marks a significant shift towards cleaner, more sustainable energy sources. This ambitious plan aims to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change by transitioning away from fossil fuels and embracing renewable energy. However, a crucial question remains at the forefront of many Americans' minds: will this transition result in higher energy prices for consumers? This article delves into the potential impacts of the new policy on electricity bills, natural gas costs, and the overall household budget, examining both the short-term and long-term implications.
Increased Investment in Renewable Energy Sources
The cornerstone of the new US energy policy is a substantial increase in investment in renewable energy sources. This involves a multifaceted approach with significant implications for consumers.
The Shift from Fossil Fuels
The policy emphasizes a decrease in reliance on fossil fuels – coal, oil, and natural gas – which currently dominate the US energy landscape. This shift has the potential to influence supply and demand dynamics significantly.
- Potential for supply shortages: Reducing domestic fossil fuel production could lead to temporary supply shortages, particularly in the short term, potentially driving up prices.
- Increased reliance on imports: A decrease in domestic fossil fuel production might necessitate increased reliance on imports, making the US more vulnerable to global energy price fluctuations.
- Impact on existing fossil fuel infrastructure: The transition away from fossil fuels will require significant adjustments to existing infrastructure, potentially leading to further costs.
Government Subsidies and Incentives
To accelerate the adoption of renewable energy, the government is implementing various subsidies and incentives. These measures aim to make renewable energy sources more economically competitive with fossil fuels.
- Tax credits: Tax credits for investing in solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy technologies reduce the upfront costs for consumers and businesses.
- Grants: Government grants provide direct financial support for renewable energy projects, further stimulating development and deployment.
- Loan programs: Low-interest loans make it easier for individuals and companies to finance renewable energy installations. However, the effectiveness of these programs depends on factors like application processes and access to capital.
Infrastructure Development
Building the necessary infrastructure to support a renewable energy-based grid is a monumental undertaking. This includes constructing new renewable energy facilities and modernizing the existing electrical grid.
- Construction costs: Building large-scale solar farms, wind turbine farms, and transmission lines involves substantial upfront capital costs.
- Land acquisition: Securing land for renewable energy projects can be complex and expensive, especially in densely populated areas.
- Permitting processes: Navigating the regulatory processes for permitting new renewable energy infrastructure can be time-consuming and costly.
- Grid modernization: Upgrading the electricity grid to handle the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources like solar and wind is crucial and requires substantial investment.
Potential Impact on Electricity Prices
The transition to renewable energy will undoubtedly impact electricity prices, though the direction and magnitude of the change are subject to debate.
Short-Term Fluctuations
In the short term, consumers may experience price fluctuations due to the challenges inherent in transitioning to a new energy system.
- Intermittency of renewable energy: Solar and wind power are intermittent sources, meaning their output fluctuates depending on weather conditions. This requires backup power sources (often fossil fuels), potentially leading to price spikes.
- Grid stability concerns: Integrating large amounts of renewable energy into the grid requires careful management to ensure stability and reliability, adding to costs.
- Need for backup power sources: Until renewable energy becomes the dominant source, the continued reliance on backup power sources, primarily natural gas, can influence electricity prices.
Long-Term Price Trends
Over the long term, the cost of renewable energy technologies is expected to continue decreasing. This could lead to price stabilization or even decreases in electricity prices.
- Technological advancements: Continuous advancements in renewable energy technologies are making them increasingly efficient and cost-effective.
- Economies of scale: As renewable energy deployment increases, economies of scale will reduce the cost of production and installation.
- Competition among renewable energy providers: Increased competition in the renewable energy sector will likely drive down prices.
Impact on Natural Gas and Other Fuel Prices
The new energy policy's impact extends beyond electricity, influencing natural gas and other fuel prices.
Natural Gas Dependence
Natural gas currently plays a crucial role in the US energy mix and is expected to continue as a transitional fuel source.
- Natural gas prices and their volatility: Natural gas prices can be volatile, influenced by factors like global supply and demand, weather conditions, and geopolitical events. The energy policy's influence on natural gas production and consumption will affect these prices.
- Impact of energy policy on natural gas production and consumption: A shift away from coal and oil could lead to increased natural gas demand in the short term, potentially keeping prices elevated.
Impact on Gasoline and Heating Oil
The ripple effects of the new energy policy can be felt in transportation and home heating costs.
- Relationship between oil and gas prices: Gasoline prices are closely tied to oil prices, which are also subject to global market forces. Changes in oil prices will indirectly influence gasoline costs.
- Influence of the policy on fuel prices: The policy's long-term impact on fuel prices is uncertain and depends on the success of renewable energy adoption in transportation and heating sectors.
Mitigation Strategies and Consumer Relief
To mitigate potential negative impacts on consumers, the government is implementing several strategies.
Energy Efficiency Programs
These programs aim to reduce overall energy consumption, thereby lessening the impact of rising energy prices.
- Tax credits for energy-efficient appliances: Tax credits for purchasing energy-efficient appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and heating systems can help consumers save money on their energy bills.
- Rebates for home improvements: Rebates for home improvements such as insulation upgrades and window replacements can significantly improve energy efficiency.
- Public awareness campaigns: Public awareness campaigns educate consumers about energy conservation techniques and the benefits of adopting energy-efficient practices.
Government Assistance Programs
The government is also providing financial assistance to low-income households to help them manage rising energy costs.
- Energy assistance programs: These programs provide direct financial assistance to low-income families to help them pay their energy bills.
- Low-income energy discounts: Utility companies often offer discounts to low-income customers to reduce the burden of rising energy prices.
- Targeted subsidies: Targeted subsidies can help low-income households invest in energy-efficient upgrades to their homes.
Conclusion
The new US energy policy represents a complex interplay between environmental ambitions and economic realities. While the transition to cleaner energy offers significant long-term environmental benefits, it may lead to short-term fluctuations in energy prices for consumers. The extent of these price increases will depend on numerous factors, including the speed of the transition, the effectiveness of government support programs, and global energy market conditions. Careful planning, technological advancements, and consumer participation are vital for a smooth and affordable transition.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the unfolding impacts of the new US energy policy on your energy bills. Research available energy efficiency programs and government assistance to mitigate potential cost increases. Understanding the complexities of the New US Energy Policy is key to navigating the changes and making informed decisions about your energy consumption.

Featured Posts
-
 Week End Sur Europe 1 Retrouvez Aurelien Veron Et Laurent Jacobelli
May 30, 2025
Week End Sur Europe 1 Retrouvez Aurelien Veron Et Laurent Jacobelli
May 30, 2025 -
 Preoccupations Des Parents D Eleves De Bouton D Or Remplacement Des Rats A Florange
May 30, 2025
Preoccupations Des Parents D Eleves De Bouton D Or Remplacement Des Rats A Florange
May 30, 2025 -
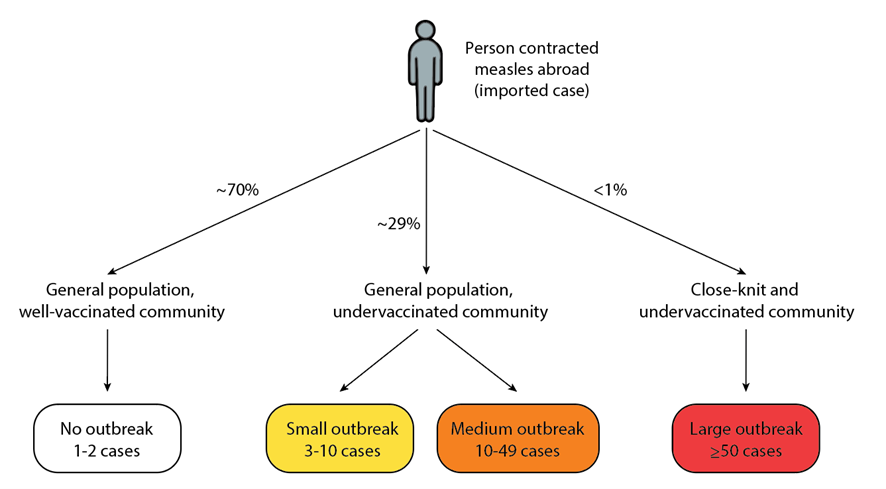 The Ongoing Threat Of Measles Factors Contributing To Persistence
May 30, 2025
The Ongoing Threat Of Measles Factors Contributing To Persistence
May 30, 2025 -
 Caida Ticketmaster 8 De Abril Ultimas Noticias Y Actualizaciones Grupo Milenio
May 30, 2025
Caida Ticketmaster 8 De Abril Ultimas Noticias Y Actualizaciones Grupo Milenio
May 30, 2025 -
 Des Moines Vehicle On Side After Police Investigated Crash
May 30, 2025
Des Moines Vehicle On Side After Police Investigated Crash
May 30, 2025
