Ontario Facing $14.6 Billion Deficit: Analysis Of Tariff Effects
Table of Contents
The Role of Import Tariffs in Widening Ontario's Deficit
Increased import tariffs have a direct and substantial impact on Ontario's deficit. These tariffs, essentially taxes on imported goods, lead to higher prices for both consumers and businesses within the province. This price inflation reduces consumer purchasing power, dampening demand and slowing economic growth. Businesses, particularly those reliant on imported raw materials and components, face increased production costs, reducing their competitiveness and potentially leading to job losses.
For example, tariffs on steel and aluminum have increased the cost of manufacturing goods across numerous sectors, impacting everything from automobiles to construction. The increased cost of imported machinery and parts also affects Ontario's manufacturing sector, making it harder to compete globally.
- Increased costs for manufacturing inputs: Higher prices for imported raw materials and components directly translate into higher production costs.
- Reduced competitiveness of Ontario businesses: Ontario businesses face a significant disadvantage when competing against those in countries with lower import costs.
- Decreased consumer purchasing power: Higher prices for imported goods reduce disposable income, leading to less consumer spending and slower economic growth.
- Potential for job losses in import-dependent sectors: Companies facing higher input costs may be forced to reduce operations or lay off workers.
Impact of Tariffs on Key Ontario Industries
Several key Ontario industries are particularly vulnerable to the effects of tariffs. The automotive sector, for example, relies heavily on imported parts and components. Tariffs on steel and aluminum, for instance, significantly impact the profitability and competitiveness of Ontario's auto manufacturers.
The agricultural sector also faces challenges, particularly with retaliatory tariffs imposed by other countries in response to Canadian tariff policies. This reduces the demand for Ontario agricultural exports, impacting farmers' incomes and the overall economic health of rural communities. Similarly, the manufacturing sector, broadly defined, suffers from increased input costs impacting numerous sub-sectors.
- Case study: Automotive industry's vulnerability to steel and aluminum tariffs: Increased input costs lead to higher vehicle prices, reducing sales and potentially impacting employment.
- Analysis of agricultural exports facing retaliatory tariffs: Reduced access to foreign markets results in decreased revenue and potential farm closures.
- Impact on manufacturing supply chains and production costs: Disruptions to supply chains and higher input costs hamper productivity and profitability.
The Export Tariff Challenge: Balancing Revenue with Competitiveness
While export tariffs can generate short-term revenue for the government, they can significantly harm Ontario's long-term economic prospects. These tariffs make Ontario products more expensive in international markets, reducing competitiveness and potentially leading to retaliatory tariffs from other countries, escalating into damaging trade wars. The potential for reduced export volumes and a decline in economic activity outweighs the short-term financial gains.
- Short-term revenue generation vs. long-term economic damage: The short-term revenue boost from export tariffs is often overshadowed by the long-term consequences of reduced exports and economic activity.
- Risk of trade wars and reduced export volumes: Imposing export tariffs can trigger retaliatory measures from other countries, leading to trade wars and significantly harming Ontario's export-oriented industries.
- The need for strategic tariff implementation: Careful consideration and strategic planning are essential to avoid unintended negative consequences.
Exploring Alternative Solutions and Fiscal Responsibility
Addressing Ontario's $14.6 billion deficit requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond relying solely on tariffs. Implementing prudent fiscal policies, including spending cuts, increased tax revenue through efficient tax policies, and economic diversification, are crucial. Investing in key sectors, such as technology and renewable energy, can foster economic growth and create jobs. Government transparency and accountability are also paramount to ensure that public funds are used responsibly and efficiently.
- Strategies for improving fiscal efficiency: Streamlining government operations, reducing administrative costs, and improving procurement processes can lead to significant savings.
- Investment in key sectors to boost economic growth: Targeted investments in innovation, technology, and clean energy can stimulate economic activity and create high-paying jobs.
- The role of effective tax policies: Well-designed tax policies can increase government revenue while minimizing their impact on economic growth.
Conclusion: Addressing Ontario's $14.6 Billion Deficit – A Call to Action
The analysis clearly shows that tariffs play a significant role in contributing to Ontario's $14.6 billion deficit. The negative impacts on key industries, reduced consumer spending, and the risk of trade wars highlight the need for a more comprehensive and sustainable approach to fiscal management. Focusing on alternative solutions, prioritizing fiscal responsibility, and fostering economic diversification are crucial steps towards resolving this fiscal challenge. Understanding the complexities of Ontario's $14.6 billion deficit requires ongoing attention. Let's continue the conversation about responsible fiscal management and the long-term effects of tariff policies on the Ontario economy. Learn more about Ontario's budget and fiscal outlook [link to relevant government resource].

Featured Posts
-
 Trump Proposes New F 55 Fighter Jet And F 22 Upgrade Details And Analysis
May 17, 2025
Trump Proposes New F 55 Fighter Jet And F 22 Upgrade Details And Analysis
May 17, 2025 -
 Angel Reese Supports Wnba Players Fight For Better Salaries
May 17, 2025
Angel Reese Supports Wnba Players Fight For Better Salaries
May 17, 2025 -
 New York Knicks Thibodeau Demands More Resolve After Crushing Defeat
May 17, 2025
New York Knicks Thibodeau Demands More Resolve After Crushing Defeat
May 17, 2025 -
 Moto Racing News Gncc Mx Sx Flat Track And Enduro Coverage
May 17, 2025
Moto Racing News Gncc Mx Sx Flat Track And Enduro Coverage
May 17, 2025 -
 Red Carpet Rule Breakers Understanding Guest Misconduct
May 17, 2025
Red Carpet Rule Breakers Understanding Guest Misconduct
May 17, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Is Refinancing Federal Student Loans Worth It The Ultimate Guide
May 17, 2025
Is Refinancing Federal Student Loans Worth It The Ultimate Guide
May 17, 2025 -
 Addressing Late Student Loan Payments To Protect Your Credit
May 17, 2025
Addressing Late Student Loan Payments To Protect Your Credit
May 17, 2025 -
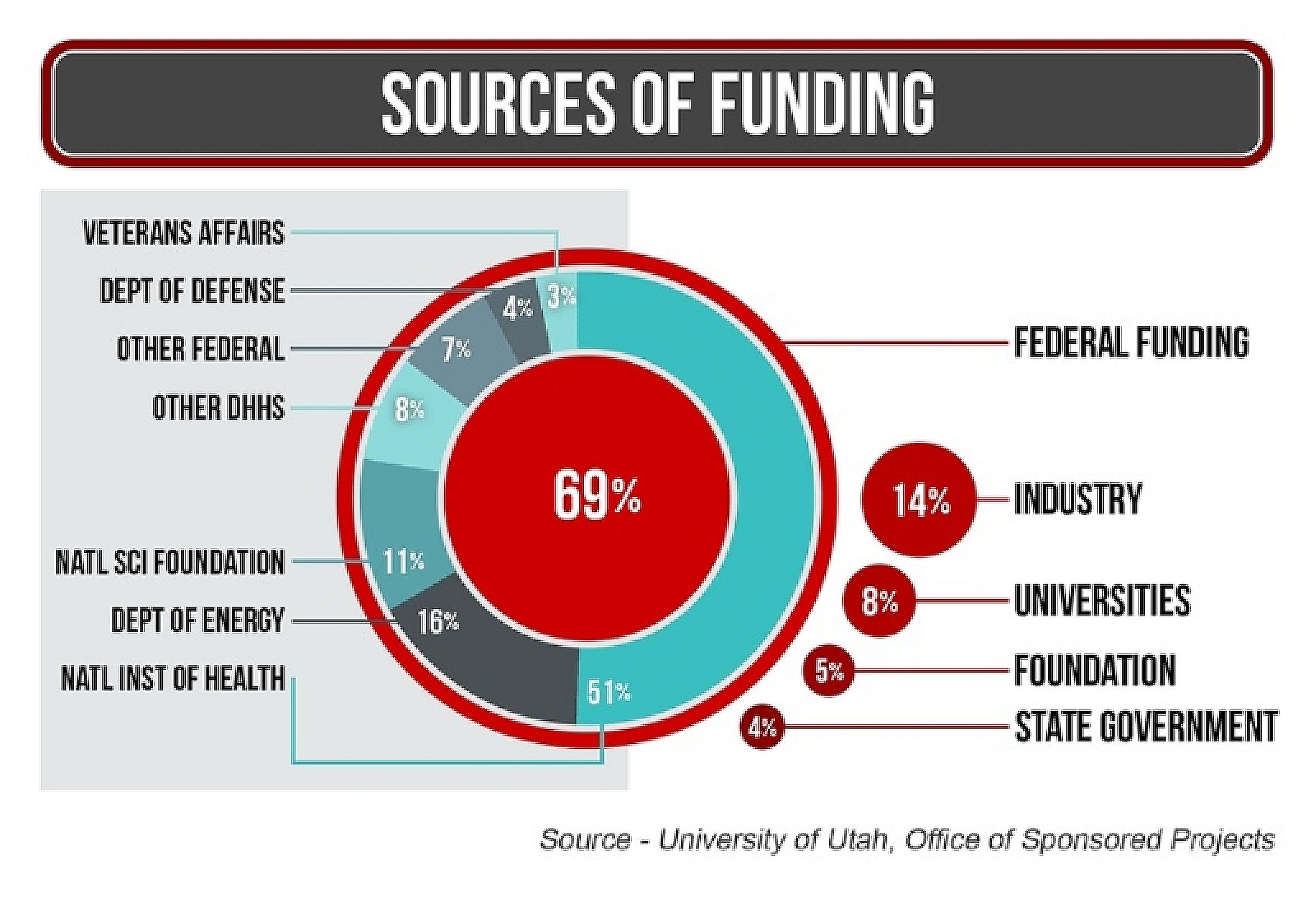 U Of U Receives 75 Million For New West Valley Hospital And Health Campus
May 17, 2025
U Of U Receives 75 Million For New West Valley Hospital And Health Campus
May 17, 2025 -
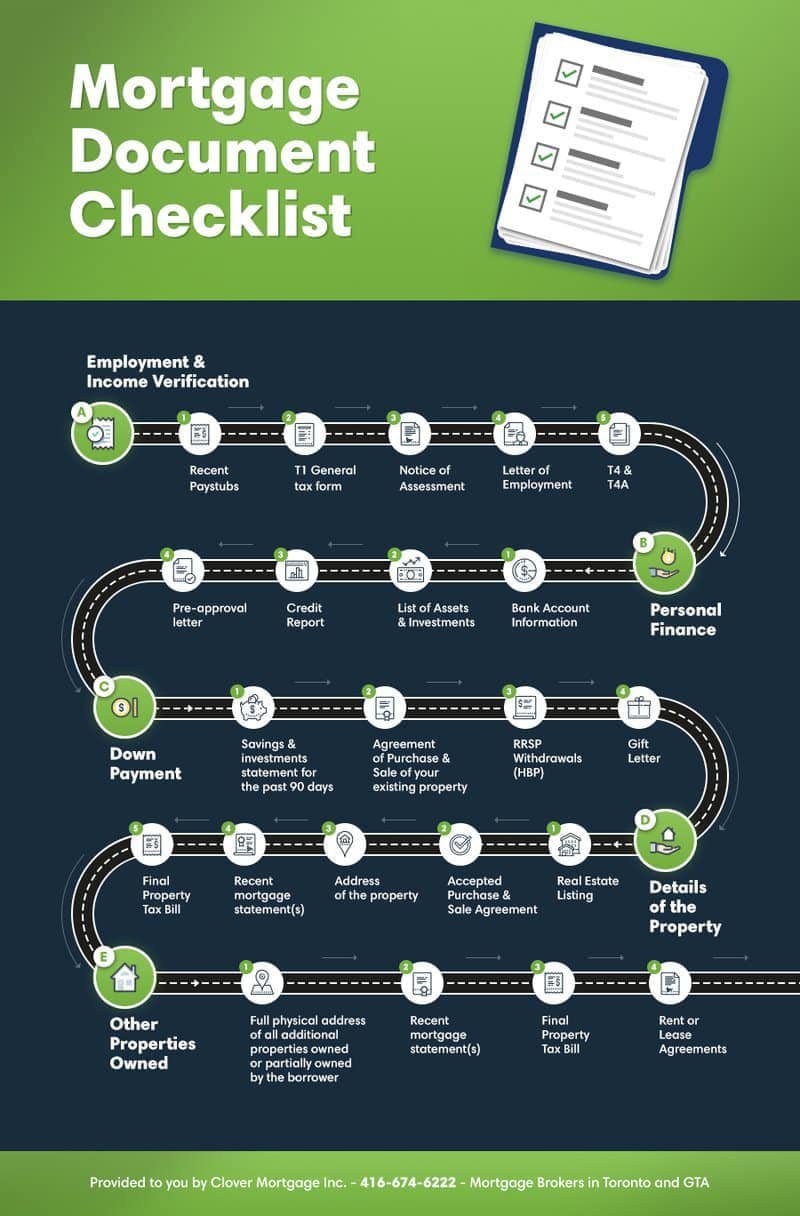 Student Loan Debt And Mortgage Qualification What You Need To Know
May 17, 2025
Student Loan Debt And Mortgage Qualification What You Need To Know
May 17, 2025 -
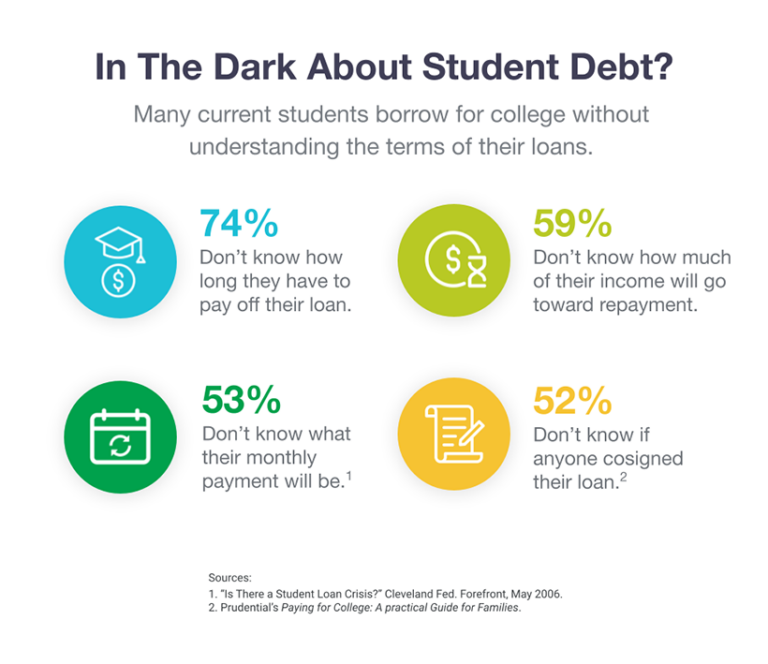 Refinance Federal Student Loans Weighing The Pros And Cons
May 17, 2025
Refinance Federal Student Loans Weighing The Pros And Cons
May 17, 2025
