Should You Take Creatine? Weighing The Pros And Cons

Table of Contents
The Proven Benefits of Creatine Supplementation
Creatine supplementation offers a range of potential advantages for athletes and fitness enthusiasts. Let's examine the key benefits supported by scientific research.
Increased Muscle Mass and Strength
Creatine's primary benefit is its ability to increase muscle mass and strength. It achieves this by increasing the availability of phosphocreatine in your muscles, fueling high-intensity activities. This leads to:
- Enhanced Muscle Power: Creatine supplementation helps your muscles produce more power during short bursts of intense activity.
- Increased Strength Gains: Studies consistently show significant gains in lean muscle mass and strength after several weeks of creatine supplementation, particularly when combined with resistance training.
- Improved Workout Capacity: You'll find you can perform more reps and sets with heavier weights, leading to faster progress in your fitness goals.
- Ideal for various athletes: This benefit is particularly relevant for weightlifters, powerlifters, bodybuilders, and athletes in sports demanding explosive power.
Enhanced Athletic Performance
Beyond muscle growth, creatine significantly improves performance in short bursts of high-intensity exercise. This includes:
- Increased Power Output: Creatine enhances your ability to generate maximal force, leading to improved sprint times, jump height, and overall athletic performance.
- Reduced Muscle Fatigue: By replenishing ATP (adenosine triphosphate), creatine helps delay muscle fatigue, allowing you to train harder and longer.
- Improved Recovery: Faster recovery times between sets and workouts contribute to overall training efficiency.
- Benefits for various sports: Creatine benefits athletes in various sports such as sprinting, weightlifting, swimming, and other high-intensity activities.
Cognitive Benefits of Creatine
While primarily known for its physical benefits, emerging research suggests creatine may offer cognitive benefits:
- Improved Memory: Some studies show that creatine can improve memory function, particularly in older adults or those with cognitive impairments.
- Enhanced Brain Function: Creatine may boost brain function by increasing creatine levels in the brain, potentially aiding in cognitive tasks requiring concentration and focus.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Preliminary research suggests potential neuroprotective effects, although more research is needed to confirm these findings.
- Ongoing Research: While promising, more extensive research is necessary to fully understand and confirm the cognitive benefits of creatine.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Creatine
While generally safe, creatine supplementation can have some potential side effects. It's crucial to be aware of these to make an informed decision.
Water Retention
Creatine's primary side effect is water retention, leading to a slight increase in body weight, mainly during the initial loading phase.
- Temporary Effect: This weight gain is typically temporary and subsides as your body adjusts to the creatine.
- Harmless for most: Water retention is generally harmless for healthy individuals.
- Management: Staying properly hydrated can help manage this effect.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Some individuals experience mild gastrointestinal discomfort when starting creatine:
- Bloating and Cramping: This can include bloating, stomach cramps, and diarrhea.
- Mitigation Strategies: Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it, along with adequate hydration, can minimize these issues.
- Individual Variation: The severity of gastrointestinal effects varies widely among individuals.
Kidney Issues (Rare)
While rare, concerns exist regarding potential kidney issues, especially in individuals with pre-existing kidney problems.
- Consult Your Doctor: Individuals with kidney disease or other health concerns should consult their doctor before taking creatine.
- Proper Hydration is Key: Maintaining adequate hydration is crucial for minimizing any potential risk to kidney function.
- Responsible Usage: Taking creatine responsibly, at the recommended dosage, significantly reduces any risk.
Choosing the Right Creatine and Dosage
Selecting the right type of creatine and following the appropriate dosage is crucial for maximizing benefits and minimizing side effects.
Creatine Monohydrate
Creatine monohydrate is the most researched and recommended form of creatine:
- Efficacy: It provides the most robust scientific evidence for its effectiveness in improving muscle mass, strength, and athletic performance.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Creatine monohydrate is widely available and generally more cost-effective than other forms of creatine.
- Purity: Choose reputable brands to ensure purity and quality.
Optimal Dosage
A common approach involves a loading phase followed by a maintenance phase:
- Loading Phase (5-7 days): Consume 20 grams of creatine daily, divided into four doses.
- Maintenance Phase: After the loading phase, maintain a daily dose of 3-5 grams.
- Individualization: Adjust dosage based on your individual response and tolerance.
Who Should Avoid Creatine?
Creatine supplementation is generally safe for healthy individuals, but certain groups should avoid it:
- Kidney Disease: Individuals with kidney disease should avoid creatine due to the potential strain on the kidneys.
- Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women: Pregnant and breastfeeding women should consult their doctor before considering creatine supplementation.
- Medical Conditions: Individuals with other medical conditions should consult their doctor before taking creatine.
Conclusion
Creatine supplementation offers numerous potential benefits for muscle growth, strength gains, and athletic performance. However, it's vital to weigh the potential side effects and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions. By understanding the pros and cons of creatine and choosing the right dosage, you can make an informed decision about whether or not creatine is right for you. If you’re ready to explore the potential of creatine for enhancing your fitness goals, consult your doctor and start your research on quality creatine supplements today. Remember to always prioritize your health and well-being. Should you take creatine? The answer depends on your individual needs and circumstances.

Featured Posts
-
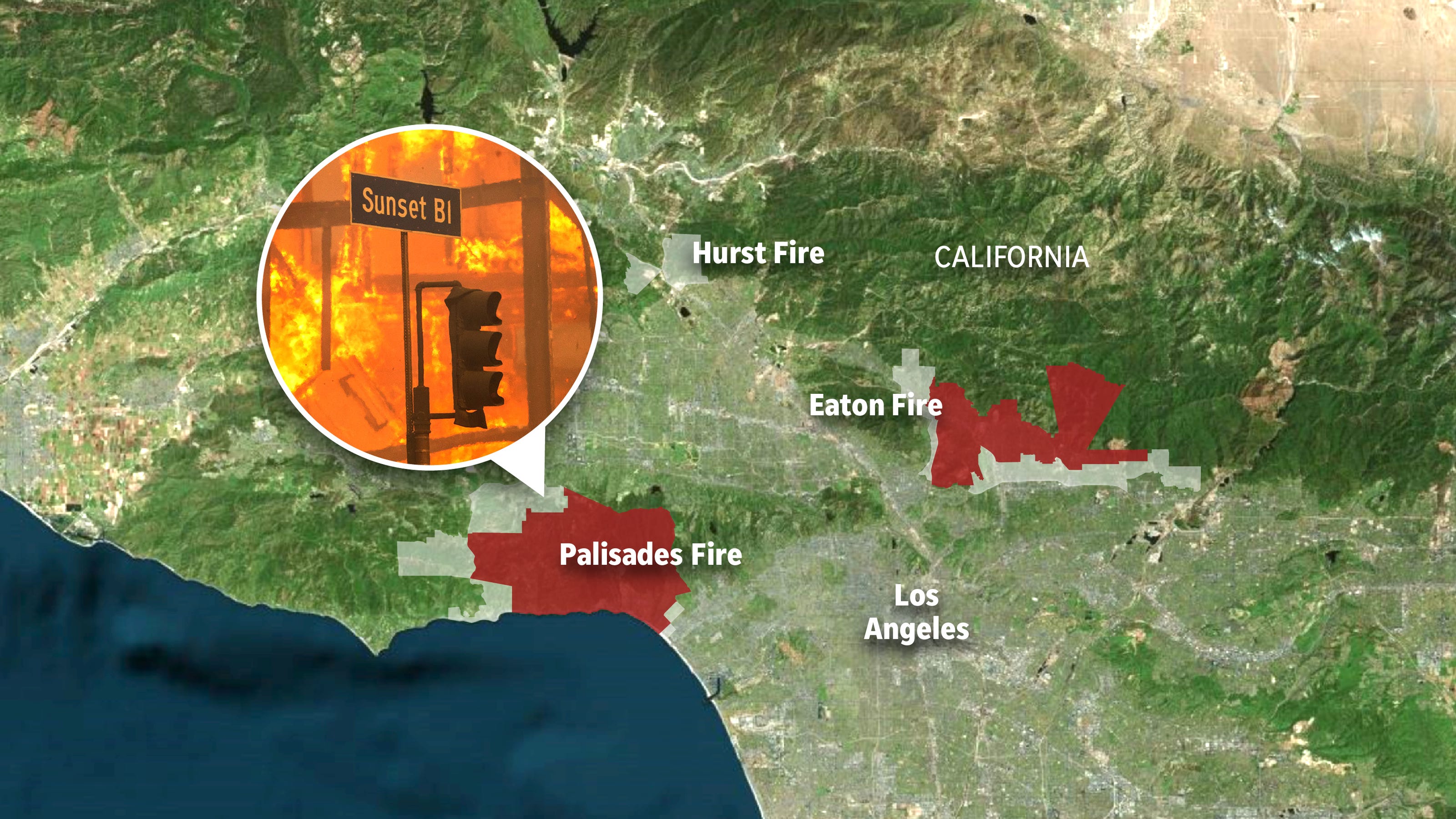 Wildfire Speculation Analyzing The Market For Los Angeles Fire Bets
May 15, 2025
Wildfire Speculation Analyzing The Market For Los Angeles Fire Bets
May 15, 2025 -
 Xi Jinpings Team Negotiates Key Us Agreement
May 15, 2025
Xi Jinpings Team Negotiates Key Us Agreement
May 15, 2025 -
 Padres Historic Mlb Win A Record Unseen Since 1889
May 15, 2025
Padres Historic Mlb Win A Record Unseen Since 1889
May 15, 2025 -
 Ind As 117 And The Future Of Insurance In India Opportunities And Challenges
May 15, 2025
Ind As 117 And The Future Of Insurance In India Opportunities And Challenges
May 15, 2025 -
 Dodgers Muncy Tries Then Abandons Torpedo Bat
May 15, 2025
Dodgers Muncy Tries Then Abandons Torpedo Bat
May 15, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 San Jose Earthquakes Opposition Scouting Report Key Strengths And Weaknesses
May 15, 2025
San Jose Earthquakes Opposition Scouting Report Key Strengths And Weaknesses
May 15, 2025 -
 Major Policy Differences Albanese And Duttons Campaign Strategies
May 15, 2025
Major Policy Differences Albanese And Duttons Campaign Strategies
May 15, 2025 -
 The Stakes Are High Comparing Albanese And Duttons Approaches
May 15, 2025
The Stakes Are High Comparing Albanese And Duttons Approaches
May 15, 2025 -
 Election 2024 Assessing The Platforms Of Albanese And Dutton
May 15, 2025
Election 2024 Assessing The Platforms Of Albanese And Dutton
May 15, 2025 -
 Dodgers Offensive Drought Leads To Cubs Win
May 15, 2025
Dodgers Offensive Drought Leads To Cubs Win
May 15, 2025
