Significant Gas Price Increase: Up Almost 20 Cents Per Gallon

Table of Contents
Causes of the Significant Gas Price Increase
Several intertwined factors have contributed to this dramatic spike in gas prices. Understanding these causes is crucial to navigating the current situation and preparing for the future.
Global Supply Chain Issues
Disruptions to the global oil supply chain are a primary driver of the current gas price increase. Geopolitical instability, particularly the ongoing conflict in Ukraine, has significantly impacted crude oil prices and availability. Sanctions imposed on major oil-producing nations have further restricted supply, creating a ripple effect across the global oil market.
- Specific Regions Affected: The Middle East, Russia, and several other regions have experienced production disruptions, impacting global crude oil prices.
- Impact of Sanctions: Sanctions on Russia, a significant oil exporter, have reduced the supply of crude oil available to the global market, pushing prices higher.
- OPEC Decisions: Decisions made by OPEC+ (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries and Russia) regarding oil production quotas can significantly influence global crude oil prices and, consequently, gas prices.
Increased Demand
The recent economic recovery, coupled with increased consumer confidence, has led to a surge in fuel demand. More people are traveling, both for leisure and work, resulting in higher consumption of gasoline and diesel. Seasonal factors, such as increased summer travel, also contribute to the heightened demand.
- Increased Travel: Post-pandemic travel has seen a significant rebound, contributing to increased gasoline consumption.
- Industrial Activity: Increased industrial activity and manufacturing also contribute to higher fuel demand.
- Seasonal Changes: Summer months typically see higher fuel demand due to increased road trips and outdoor activities.
Refining Capacity Constraints
Limitations in refining capacity are exacerbating the situation. Several refineries are undergoing maintenance or facing operational challenges, reducing the amount of gasoline produced and impacting the gasoline supply. This shortage further contributes to the gas price increase.
- Refinery Maintenance: Scheduled and unscheduled maintenance at refineries can temporarily reduce processing capacity.
- Refinery Closures: The closure of certain refineries due to various factors reduces overall gasoline production.
- Operational Challenges: Unexpected operational issues at refineries can lead to temporary production slowdowns.
Impact of the Gas Price Increase
The significant gas price increase has far-reaching consequences, affecting both consumers and businesses.
Impact on Consumers
Higher fuel costs directly impact household budgets. Increased commuting costs, coupled with higher prices for goods and services (due to increased transportation costs), are putting a strain on many families. This gas price increase is contributing to inflation and reducing consumer purchasing power.
- Increased Commuting Costs: For those who commute daily, the gas price increase significantly impacts their transportation expenses.
- Higher Prices for Goods and Services: Increased transportation costs for businesses translate to higher prices for consumers across a wide range of products.
- Impact on Household Budgets: The increase in fuel costs eats into household disposable income, forcing families to make difficult choices.
Impact on Businesses
Businesses, particularly those in the transportation and logistics sectors, are heavily impacted by the increased fuel costs. Higher shipping costs lead to increased prices for consumers and can even threaten the viability of some businesses.
- Increased Shipping Costs: Transportation companies face significantly higher operating expenses, impacting their profitability.
- Price Increases for Consumers: Businesses often pass on increased fuel costs to consumers, leading to higher prices for goods and services.
- Potential Business Closures: For some businesses, particularly smaller ones with tight margins, the increased fuel costs can be unsustainable, leading to potential closures.
Potential Solutions and Future Outlook
Addressing this significant gas price increase requires a multifaceted approach.
Government Policies
Governments can implement various policies to mitigate the impact of high gas prices. These include tax cuts on gasoline, subsidies for fuel-efficient vehicles, and investments in public transportation. However, the effectiveness and long-term implications of such policies need careful consideration.
- Fuel Tax Cuts: Temporary reductions in fuel taxes can provide immediate relief to consumers.
- Subsidies for Fuel-Efficient Vehicles: Incentivizing the purchase of fuel-efficient vehicles can reduce long-term reliance on fossil fuels.
- Investment in Public Transportation: Improving public transportation options can reduce individual reliance on personal vehicles.
Alternative Energy Sources
The transition towards alternative energy sources, such as electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy, is crucial for reducing long-term reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating future gas price volatility. Increased investment in renewable energy infrastructure and EV adoption are vital steps.
- Electric Vehicle Adoption: Increasing the adoption of electric vehicles reduces demand for gasoline.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Investing in renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
- Alternative Fuels: Exploring alternative fuels like biofuels can diversify energy sources and reduce reliance on oil.
Predicting Future Gas Prices
Predicting future gas prices is challenging due to the volatile nature of the global oil market. Geopolitical events, economic growth, and OPEC decisions are among the key factors that will influence future fuel price movements. While a short-term decrease is possible, sustained price stability will require a combination of increased supply, reduced demand, and a shift towards cleaner energy sources.
- Geopolitical Events: International conflicts and political instability can significantly impact oil prices.
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth generally leads to increased demand for oil.
- OPEC Decisions: OPEC production quotas continue to play a significant role in shaping global oil prices.
Conclusion
The significant gas price increase is a result of a complex interplay of global supply chain issues, increased demand, and refining capacity constraints. This has created considerable financial strain on consumers and businesses. To navigate this challenge, it's crucial to monitor gas price increases, manage your fuel budget, and understand the factors affecting gas prices. By diversifying energy sources, investing in renewable energy, and promoting fuel efficiency, we can strive for a more sustainable and price-stable energy future. The gravity of this situation necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the factors driving this significant gas price increase.

Featured Posts
-
 Juergen Klopp Bir Efsanenin Yeniden Dogusu Mu
May 22, 2025
Juergen Klopp Bir Efsanenin Yeniden Dogusu Mu
May 22, 2025 -
 The Goldbergs Character Analysis And Show Evolution
May 22, 2025
The Goldbergs Character Analysis And Show Evolution
May 22, 2025 -
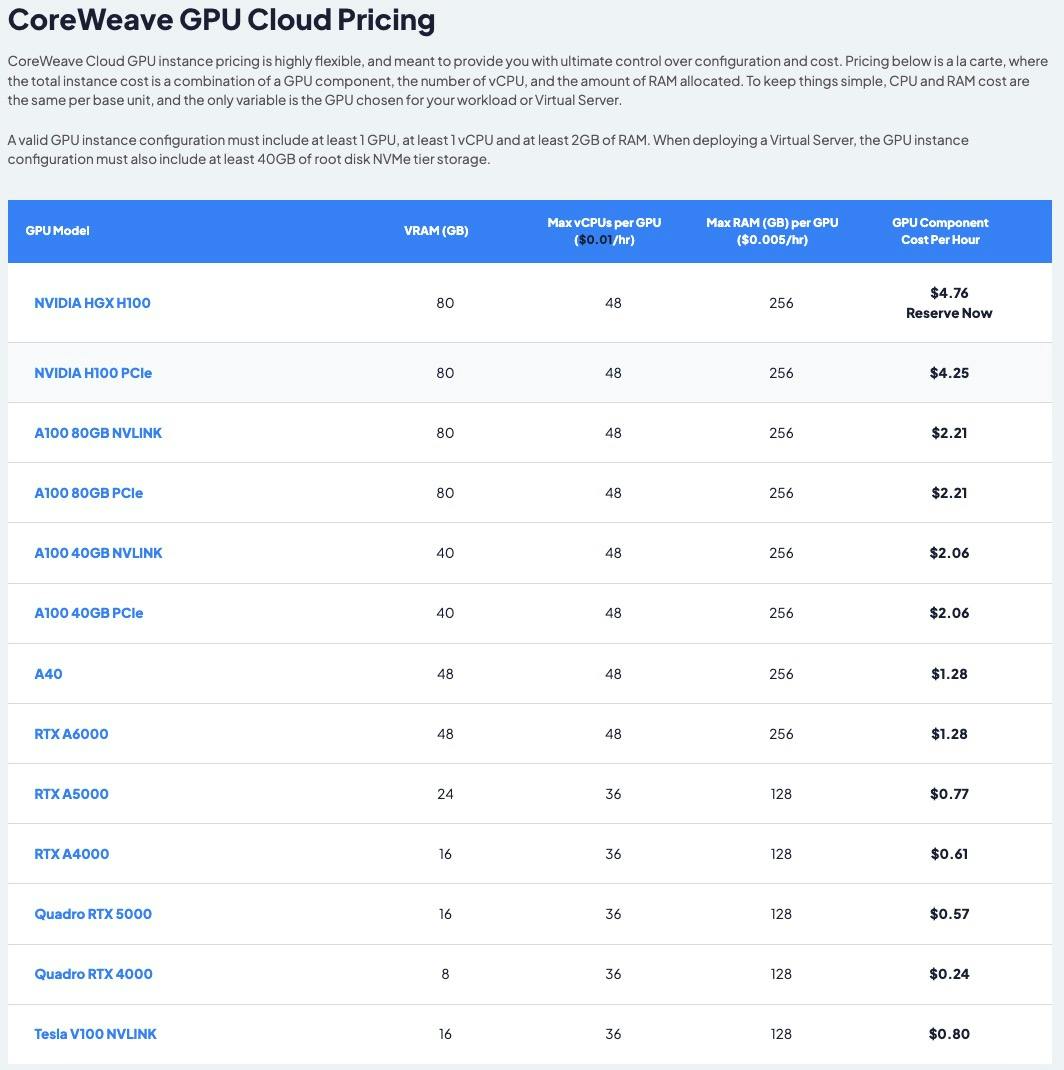 Understanding The Current Core Weave Stock Situation
May 22, 2025
Understanding The Current Core Weave Stock Situation
May 22, 2025 -
 Improving Wilderness Safety Collaborative Efforts With Bear Spray And Training
May 22, 2025
Improving Wilderness Safety Collaborative Efforts With Bear Spray And Training
May 22, 2025 -
 Bgt Blockbusters What Made It Special
May 22, 2025
Bgt Blockbusters What Made It Special
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 On 98 5 The Fox Analysis And Commentary
May 23, 2025
Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 On 98 5 The Fox Analysis And Commentary
May 23, 2025 -
 5 The Foxs Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 A Comprehensive Overview
May 23, 2025
5 The Foxs Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 A Comprehensive Overview
May 23, 2025 -
 Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 Key Updates From 98 5 The Fox
May 23, 2025
Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 Key Updates From 98 5 The Fox
May 23, 2025 -
 Analysis Of Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 96 Focus On The Rocket
May 23, 2025
Analysis Of Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 96 Focus On The Rocket
May 23, 2025 -
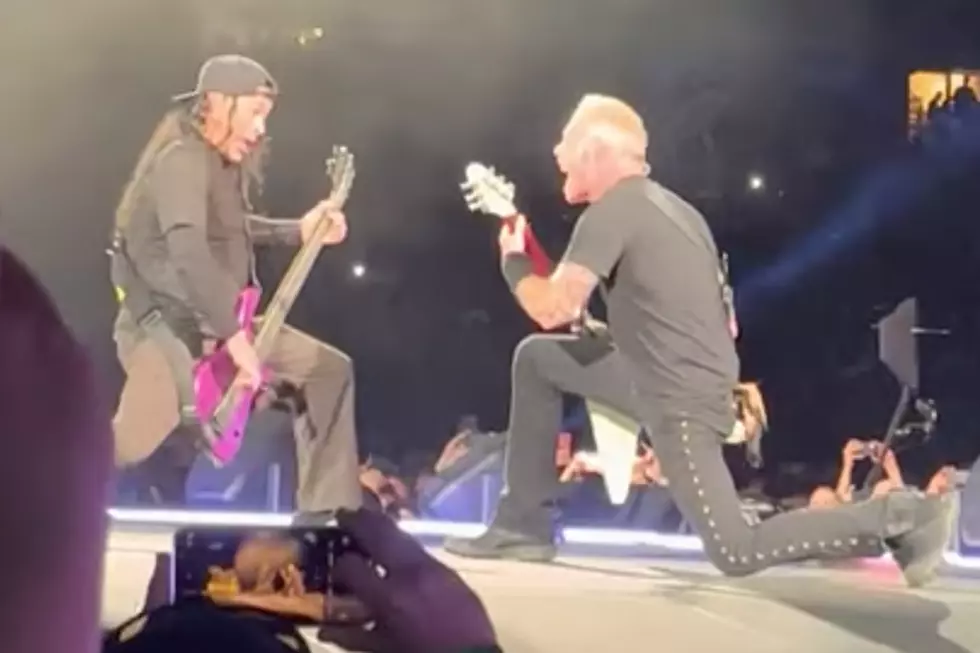 Metallica To Play Two Nights At Dublins Aviva Stadium In June 2026
May 23, 2025
Metallica To Play Two Nights At Dublins Aviva Stadium In June 2026
May 23, 2025
