Swiss Landslide Threat: Livestock Evacuated By Hoof And Helicopter

Table of Contents
The Imminent Landslide Threat in Switzerland
The landslide threat emerged in the [Specific Region of the Swiss Alps – replace with actual location if known], an area known for its geological instability. The risk assessment, conducted by [Name of Organization responsible for assessment – e.g., Swiss Federal Institute for Forest, Snow and Landscape Research WSL], identified a high probability of a major rockslide or debris flow due to [Specific geological factors contributing to the risk – e.g., heavy rainfall, weakened soil structure, etc.]. The effectiveness of the early warning system was crucial in this situation, providing timely alerts to local farmers and enabling swift action.
- Type of Landslide: [Insert type of landslide, e.g., a combination of rockfall and debris flow]
- Affected Area: Approximately [Size of affected area] near [Description of proximity to settlements, e.g., several farms and a small village].
- Previous Incidents: The region has a history of smaller landslides, highlighting the ongoing geological instability and the need for continuous monitoring. [Cite any past incidents if possible].
- Communication: Alerts were disseminated via [Methods used for communication – e.g., text messages, local radio, sirens] ensuring timely warning to the affected communities and farmers.
Evacuating Livestock: A Two-Pronged Approach
Evacuating the livestock presented a significant logistical challenge. A two-pronged approach was employed, combining traditional herding methods with the rapid deployment of helicopters for swift relocation. This dual strategy proved essential in ensuring the safety and welfare of the animals.
- Number of Animals: Over [Number] animals were successfully evacuated, including [Types of livestock involved – e.g., cows, sheep, goats].
- Herding Challenges: The steep and challenging terrain presented difficulties in herding the animals, requiring experienced shepherds and careful coordination. [Describe specific challenges – e.g., difficult-to-access areas, agitated animals].
- Helicopter Operation: [Number] helicopters were deployed, each capable of carrying [Number] animals at a time. [Describe safety measures taken – e.g., specialized animal crates, trained pilots].
- Animal Welfare: [State measures to ensure animal welfare, e.g., regular checks on animals during transport, provision of water and food].
- Injuries: Thankfully, no significant injuries were reported among the animals or human personnel involved in the evacuation.
The Role of Technology in the Rescue
Technology played a crucial role in mitigating the landslide threat and ensuring a successful evacuation. Drone surveillance provided real-time imagery of the unstable area, aiding in risk assessment and guiding the evacuation efforts. GPS trackers on some livestock aided in monitoring their location and ensuring none were left behind.
- Drone Surveillance: High-resolution drone imagery allowed for precise identification of unstable areas and potential hazards, improving the safety of both humans and animals.
- GPS Tracking: GPS trackers attached to select animals provided real-time location data, enhancing the efficiency of the evacuation and enabling precise monitoring.
- Communication Technology: [Specify communication technology – e.g., two-way radios, satellite phones] ensured seamless coordination between the different teams involved in the rescue operation.
The Aftermath and Lessons Learned
Following the successful evacuation, a post-landslide assessment was conducted to evaluate the damage and plan for future mitigation efforts. The incident reinforced the importance of proactive risk assessment and community involvement in disaster preparedness.
- Damage Assessment: [Describe any damage caused by the landslide – e.g., minimal damage to infrastructure, some disruption to local roads].
- Safety Measures: [Detail measures taken to ensure ongoing safety – e.g., temporary road closures, continued landslide monitoring].
- Landslide Mitigation: Plans are underway for long-term landslide mitigation and prevention strategies in the region, including [Specific mitigation measures – e.g., improved drainage systems, land stabilization techniques].
- Community Resilience: The successful evacuation demonstrated the importance of community participation and collaboration in disaster response, improving overall resilience.
Conclusion
The Swiss landslide threat underscored the critical need for proactive landslide risk assessment, swift emergency response, and innovative solutions to protect livestock and communities. The combined use of traditional herding techniques and advanced technology proved crucial in this successful evacuation, showcasing the power of collaboration and preparedness. Learn more about the ongoing efforts to mitigate landslide risks in Switzerland and how communities are preparing for future threats by searching for "Swiss landslide prevention" or "Swiss livestock safety".

Featured Posts
-
 Macaulay Culkin And Kieran Culkins Mothers Financial Struggle A Report
May 23, 2025
Macaulay Culkin And Kieran Culkins Mothers Financial Struggle A Report
May 23, 2025 -
 Johnson Mattheys Catalyst Technologies Business Acquired By Honeywell A Strategic Expansion
May 23, 2025
Johnson Mattheys Catalyst Technologies Business Acquired By Honeywell A Strategic Expansion
May 23, 2025 -
 Historic Win For Zimbabwe Sylhet Test Seals Away Victory
May 23, 2025
Historic Win For Zimbabwe Sylhet Test Seals Away Victory
May 23, 2025 -
 Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 Essential Information For Truck Drivers From Rock 106 1
May 23, 2025
Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 Essential Information For Truck Drivers From Rock 106 1
May 23, 2025 -
 F1 Russell Dominates Final Day Of Testing
May 23, 2025
F1 Russell Dominates Final Day Of Testing
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 2002 Submarine Bribery Case French Prosecutors Accuse Malaysias Ex Pm Najib
May 23, 2025
2002 Submarine Bribery Case French Prosecutors Accuse Malaysias Ex Pm Najib
May 23, 2025 -
 Najib Razak French Investigation Links Former Malaysian Pm To Submarine Scandal
May 23, 2025
Najib Razak French Investigation Links Former Malaysian Pm To Submarine Scandal
May 23, 2025 -
 Malaysia Ex Pm Najibs Alleged Role In 2002 French Submarine Bribery Scandal
May 23, 2025
Malaysia Ex Pm Najibs Alleged Role In 2002 French Submarine Bribery Scandal
May 23, 2025 -
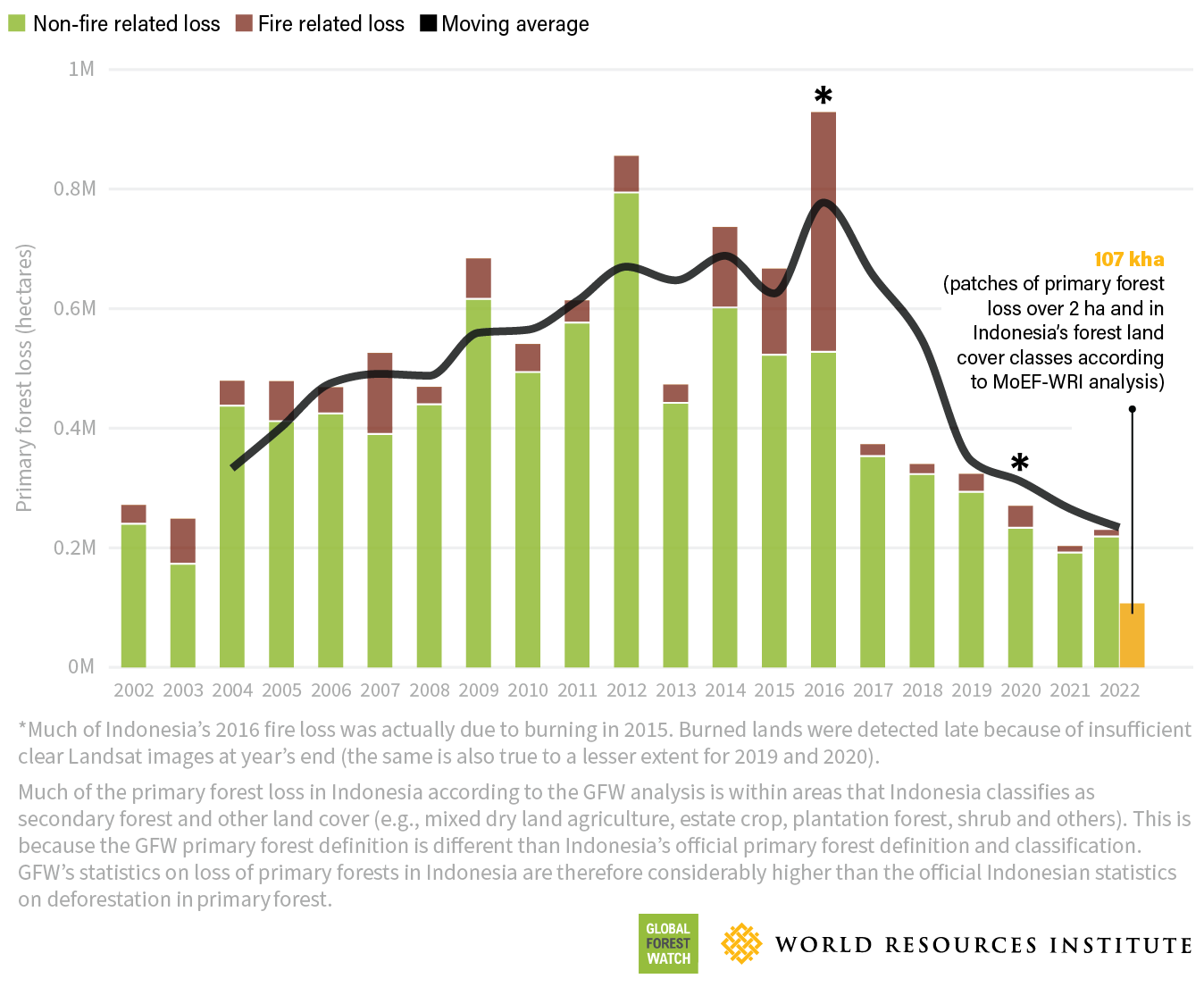 Unprecedented Global Forest Loss The Devastating Impact Of Wildfires
May 23, 2025
Unprecedented Global Forest Loss The Devastating Impact Of Wildfires
May 23, 2025 -
 Global Forest Destruction Wildfires Push Losses To Unprecedented Levels
May 23, 2025
Global Forest Destruction Wildfires Push Losses To Unprecedented Levels
May 23, 2025
