Unprecedented Global Forest Loss: The Devastating Impact Of Wildfires
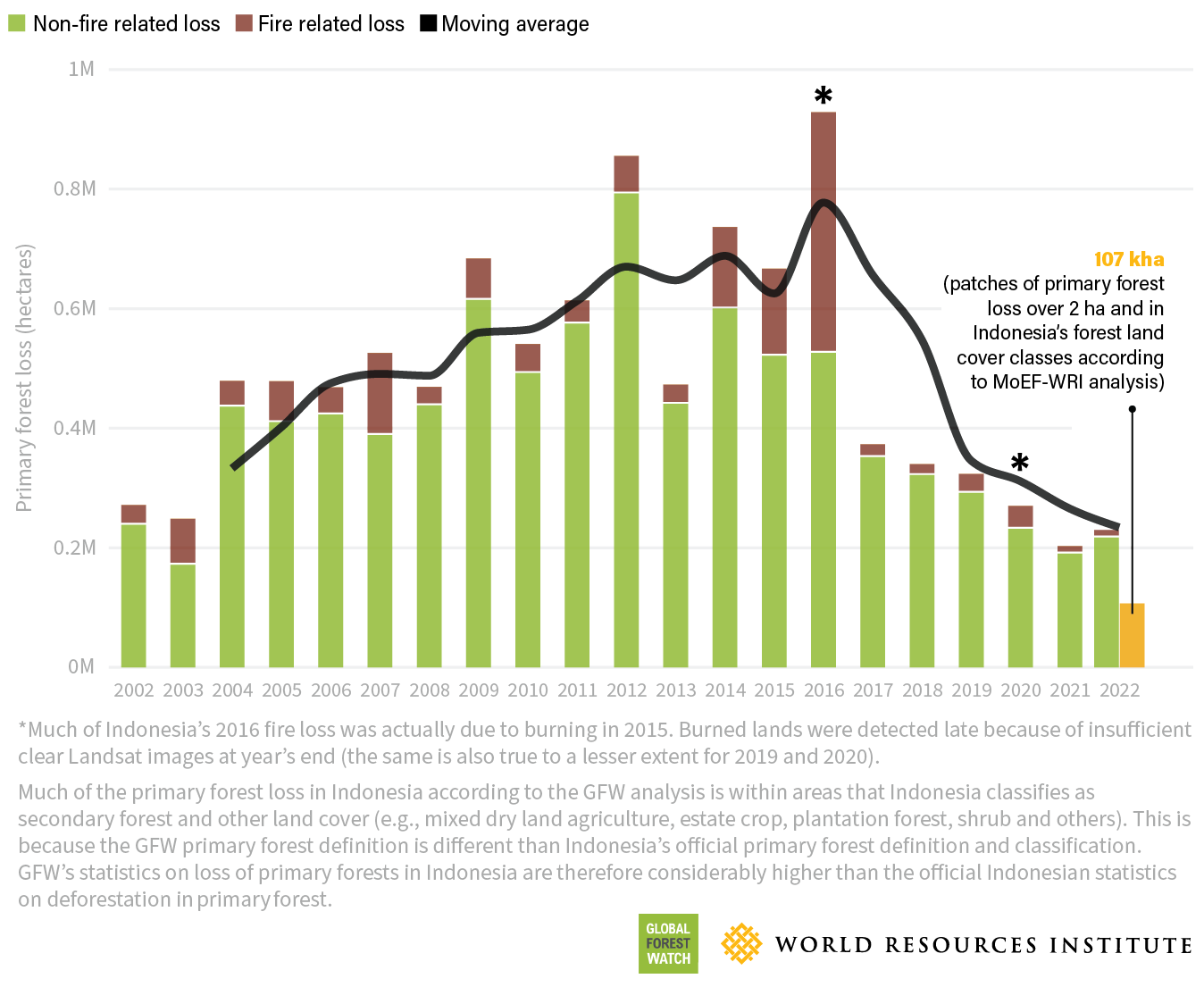
Table of Contents
The Rising Frequency and Intensity of Wildfires
The increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires globally are inextricably linked to climate change. Rising global temperatures, prolonged droughts, and increasingly erratic weather patterns create ideal conditions for ignition and rapid fire spread. These factors are contributing to longer fire seasons and more extensive burn areas.
- Increased average temperatures: Higher temperatures dry out vegetation, creating readily available fuel for wildfires.
- Longer fire seasons: Warmer springs and autumns extend the period when conditions are favorable for wildfires.
- Increased wind speeds: Stronger winds accelerate the spread of fires, making them harder to contain.
- Examples of devastating wildfires: Recent years have witnessed catastrophic wildfires across the globe, including the devastating Australian bushfires of 2019-2020, the Amazon rainforest fires, and numerous large-scale wildfires in California, all contributing significantly to global forest loss. These events highlight the urgent need for effective wildfire management strategies.
The Ecological Consequences of Global Forest Loss
The ecological consequences of rampant wildfires and the resulting global forest loss are devastating and far-reaching. The destruction of forests leads to catastrophic biodiversity loss, habitat destruction, and species extinction. The intricate balance of ecosystems is shattered, triggering a cascade of negative effects.
- Loss of plant and animal species: Countless plant and animal species are directly killed by wildfires, while many more lose their habitat and face extinction.
- Disruption of carbon cycles: Forests act as vital carbon sinks. Their destruction releases vast quantities of stored carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change and contributing to a vicious cycle of increased global forest loss.
- Soil erosion and degradation: The loss of vegetation leaves soil exposed to the elements, leading to erosion and loss of fertility.
- Impact on water cycles and water availability: Forests play a crucial role in regulating water cycles. Their destruction disrupts rainfall patterns and reduces water availability, impacting both ecosystems and human populations.
The Socioeconomic Impacts of Wildfires and Forest Loss
The socioeconomic impacts of wildfires and associated global forest loss are substantial and far-reaching. The costs extend far beyond immediate firefighting efforts, impacting economies, livelihoods, and human health.
- Costs of firefighting and emergency response: The financial burden of combating wildfires is enormous, stretching the resources of governments and communities.
- Damage to infrastructure and property: Wildfires destroy homes, businesses, and vital infrastructure, causing billions of dollars in damage.
- Loss of tourism revenue: The destruction of forests significantly impacts tourism, a crucial sector in many regions.
- Impacts on indigenous communities and their traditional livelihoods: Indigenous communities often bear the brunt of wildfire impacts, losing their homes, traditional lands, and sources of sustenance.
- Health consequences of smoke inhalation and air pollution: Wildfire smoke causes respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular problems, and other health issues, impacting millions of people.
Mitigation and Conservation Strategies to Combat Global Forest Loss
Combating global forest loss requires a multifaceted approach focusing on both prevention and restoration. Effective strategies include improved forest management, early warning systems, and international cooperation.
- Improved forest management techniques: Sustainable forest management practices, including controlled burns and thinning, can reduce fuel loads and mitigate the risk of large-scale wildfires.
- Early warning systems and rapid response strategies: Advanced technologies and early warning systems are crucial for detecting and responding to wildfires quickly and effectively.
- Controlled burns to reduce fuel loads: Prescribed burns, conducted under controlled conditions, can help reduce the amount of combustible material in forests.
- Reforestation and afforestation programs: Planting trees is vital for restoring lost forests and sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- International cooperation and agreements: Global collaboration is essential to address the transboundary nature of wildfire threats and to implement effective policies for forest conservation.
Conclusion
The unprecedented scale of global forest loss due to wildfires presents a grave threat to our planet's ecosystems and human societies. The multifaceted impacts, from biodiversity loss to economic devastation and health crises, demand urgent action. We must strengthen wildfire prevention and mitigation efforts, invest in reforestation and afforestation, and foster international cooperation to combat this critical issue. We must all play a part in reducing global forest loss. Learn more and take action today! Support organizations working to protect forests, advocate for policies that promote sustainable forest management and climate change mitigation, and join the fight against the devastating effects of global forest loss.

Featured Posts
-
 Antonys Near Miss How He Almost Joined Manchester Uniteds Biggest Rivals
May 23, 2025
Antonys Near Miss How He Almost Joined Manchester Uniteds Biggest Rivals
May 23, 2025 -
 Bitcoin Price Surge Positive Us Regulation Signals Drive Record High
May 23, 2025
Bitcoin Price Surge Positive Us Regulation Signals Drive Record High
May 23, 2025 -
 Freddie Flintoff Confirms Disney Documentary About His Crash
May 23, 2025
Freddie Flintoff Confirms Disney Documentary About His Crash
May 23, 2025 -
 Vanja Mijatovic Potresna Ispovest O Razvodu I Borbi S Medijima
May 23, 2025
Vanja Mijatovic Potresna Ispovest O Razvodu I Borbi S Medijima
May 23, 2025 -
 Man United News Tagliafico Points Finger At Players For Ten Hags Underperformance
May 23, 2025
Man United News Tagliafico Points Finger At Players For Ten Hags Underperformance
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Is It Going To Rain In Nyc During Memorial Day Weekend
May 23, 2025
Is It Going To Rain In Nyc During Memorial Day Weekend
May 23, 2025 -
 Memorial Day Weekend 2025 Everything You Need To Know
May 23, 2025
Memorial Day Weekend 2025 Everything You Need To Know
May 23, 2025 -
 Memorial Day Weekend Weather Forecast For New York City
May 23, 2025
Memorial Day Weekend Weather Forecast For New York City
May 23, 2025 -
 What Date Is Memorial Day In 2025 Planning Your Three Day Weekend
May 23, 2025
What Date Is Memorial Day In 2025 Planning Your Three Day Weekend
May 23, 2025 -
 Nyc Memorial Day Weekend Weather Will It Rain
May 23, 2025
Nyc Memorial Day Weekend Weather Will It Rain
May 23, 2025
