The Bank Of Canada's Monetary Policy: A Missed Opportunity? Rosenberg's Analysis.
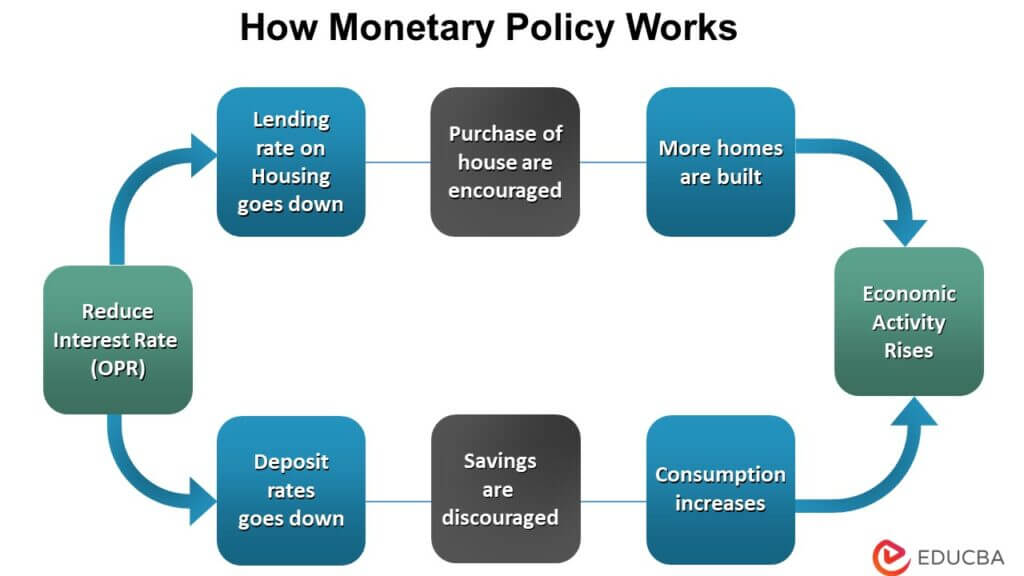
Table of Contents
Rosenberg's Critique of the Bank of Canada's Interest Rate Hikes
The Speed and Magnitude of Rate Increases
Did the Bank of Canada raise interest rates too quickly and aggressively? Rosenberg's analysis likely argues that the sharp increases, while aiming to curb inflation, risked triggering a more significant economic downturn. The rapid pace of rate hikes, unprecedented in recent decades, has raised concerns about their impact on various sectors of the Canadian economy.
- Analysis of the impact on consumer spending: Higher interest rates directly impact borrowing costs, potentially leading to reduced consumer spending and a slowdown in economic growth. This is particularly relevant given the already high levels of household debt in Canada. The Bank of Canada's monetary policy decisions directly influence the cost of mortgages and other loans, impacting Canadians' purchasing power and their ability to finance large purchases.
- Examination of the housing market’s vulnerability: The Canadian housing market, historically sensitive to interest rate changes, faced significant pressure. Rapid interest rate increases could lead to a sharper correction than anticipated, affecting both homeowners and the broader economy. The potential for a housing market crash adds complexity to the evaluation of the Bank of Canada's monetary policy effectiveness.
- Discussion of the potential for increased unemployment: A significant economic slowdown resulting from aggressive interest rate hikes could lead to increased unemployment. Businesses might cut back on hiring or even lay off workers in response to reduced demand. This is a crucial social and economic consequence to consider when analyzing the Bank of Canada's monetary policy choices.
The Effectiveness of Interest Rate Hikes in Controlling Inflation
Did the interest rate hikes achieve their intended goal of effectively controlling inflation, or were other factors at play? Rosenberg likely contends that factors beyond interest rate control significantly influenced inflation, rendering the aggressive approach less effective. Simply raising interest rates might not address the root causes of inflation in a complex global economy.
- Analysis of supply chain disruptions' contribution to inflation: Global supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by the pandemic, played a significant role in driving up prices. Interest rate hikes have limited impact on supply-side issues. The Bank of Canada's monetary policy needed to consider this factor alongside its interest rate decisions.
- Examination of the impact of global energy prices: Soaring global energy prices, influenced by geopolitical factors, significantly contributed to inflation. The Bank of Canada's ability to influence these global factors is limited. This external factor requires careful consideration when assessing the effectiveness of the Bank's monetary policy actions.
- Discussion of the role of wage growth: Wage growth, while contributing to inflationary pressures, also reflects strong labor market conditions. Suppressing wage growth through monetary policy could have unintended negative consequences, hindering economic growth and potentially exacerbating inequality. The Bank of Canada's monetary policy must navigate the delicate balance between controlling inflation and supporting employment.
Alternative Monetary Policy Approaches Considered by Rosenberg
Focus on Quantitative Tightening (QT)
Did the Bank of Canada place sufficient emphasis on QT as a complementary tool to interest rate adjustments? Rosenberg might suggest that a greater focus on QT could have been more effective. QT, involving reducing the Bank's balance sheet, can be a powerful tool to control money supply and curb inflation.
- Explanation of how QT works: QT involves selling government bonds held by the Bank of Canada, reducing the money supply and pushing up long-term interest rates. This complements the effects of short-term interest rate increases.
- Comparison of QT's effectiveness versus interest rate hikes: QT might have offered a more gradual approach, potentially minimizing the risk of a sharp economic downturn. A balanced approach combining QT and interest rate adjustments might have been more effective in controlling inflation while minimizing economic disruption.
- Analysis of the potential risks and benefits of increased QT: While QT can be effective, it also carries risks. Rapid QT can disrupt financial markets and negatively impact economic growth. Finding the optimal balance between QT and other monetary policy tools is crucial.
Forward Guidance and Communication Strategy
Was the Bank of Canada's communication strategy regarding future monetary policy clear and effective? Rosenberg might argue that inconsistencies or unclear messaging could have undermined the effectiveness of their policy. Clear and consistent communication is vital for guiding market expectations and ensuring policy effectiveness.
- Evaluation of the transparency of the Bank's communication: The clarity and transparency of the Bank's communications directly impact market confidence and investor behavior. A lack of transparency can lead to uncertainty and volatility in the markets.
- Analysis of market reactions to the Bank's statements: Monitoring market reactions to the Bank's statements is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of its communication strategy. Unexpected market reactions can indicate a need for improved communication.
- Discussion on potential improvements to communication strategies: Improved communication strategies could involve more frequent and transparent updates, clearer explanations of policy decisions, and more proactive engagement with stakeholders.
The Broader Economic Implications of Rosenberg's Analysis
Impact on Economic Growth
What are the long-term implications of the Bank of Canada's monetary policy for economic growth in Canada? Rosenberg's assessment might highlight potential long-term consequences of the aggressive approach. The Bank of Canada's choices have far-reaching implications for Canada's economic future.
- Analysis of potential GDP growth reduction: Aggressive interest rate hikes could lead to a sustained reduction in GDP growth, impacting the overall prosperity of the nation. This is a critical aspect for assessing the long-term consequences of the Bank's actions.
- Discussion of the impact on business investment: Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing for businesses, potentially leading to reduced investment and hindered economic expansion. This impacts job creation and future economic potential.
- Examination of potential repercussions on job creation: A slower economic growth rate due to restrictive monetary policy can result in reduced job creation, leading to higher unemployment and social challenges. The impact on employment is a key concern when evaluating the Bank's policy decisions.
Implications for the Canadian Dollar
How has the Bank of Canada's monetary policy affected the value of the Canadian dollar? Rosenberg may offer analysis on the impact of interest rate decisions on currency exchange rates. Changes in interest rates influence capital flows and currency values.
- Analysis of fluctuations in the Canadian dollar: The Canadian dollar's value is directly influenced by interest rate decisions, impacting exports and imports. Understanding these fluctuations is crucial for assessing the wider economic consequences of monetary policy.
- Discussion of the impact on exports and imports: A stronger Canadian dollar, potentially resulting from higher interest rates, can negatively impact exports by making Canadian goods more expensive internationally. Conversely, it could make imports cheaper.
- Examination of the long-term consequences for the Canadian economy: The long-term effects of currency fluctuations stemming from the Bank of Canada's monetary policy require careful consideration. These fluctuations impact trade balances and overall economic stability.
Conclusion
David Rosenberg's critique of the Bank of Canada's monetary policy offers a compelling alternative perspective on the recent economic challenges faced by Canada. By examining the speed and magnitude of interest rate hikes, alternative strategies, and broader economic implications, his analysis highlights potential areas where the Bank might have missed opportunities for a more effective response. Understanding Rosenberg's perspective is crucial for informed discussions about future Bank of Canada's monetary policy decisions and for shaping more effective strategies to navigate future economic uncertainty. Further investigation into the specific details of Rosenberg’s analysis is encouraged to fully grasp the implications of his arguments for the Bank of Canada's monetary policy.

Featured Posts
-
 Goldblum Family Outing A Day At The Football Match In Italy
Apr 29, 2025
Goldblum Family Outing A Day At The Football Match In Italy
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Analyzing The Zombie Building Problem In Chicagos Office Market
Apr 29, 2025
Analyzing The Zombie Building Problem In Chicagos Office Market
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Secure Your Capital Summertime Ball 2025 Tickets The Ultimate Guide
Apr 29, 2025
Secure Your Capital Summertime Ball 2025 Tickets The Ultimate Guide
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Is The Venture Capital Secondary Market Overheated A Current Analysis
Apr 29, 2025
Is The Venture Capital Secondary Market Overheated A Current Analysis
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Actor Jeff Goldblum Launches Music Career With New Album
Apr 29, 2025
Actor Jeff Goldblum Launches Music Career With New Album
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Trump Administrations Oil Policies Balancing Low Prices And Industry Support
May 12, 2025
Trump Administrations Oil Policies Balancing Low Prices And Industry Support
May 12, 2025 -
 Trumps Cheap Oil Policy Praise And Conflict With The Energy Sector
May 12, 2025
Trumps Cheap Oil Policy Praise And Conflict With The Energy Sector
May 12, 2025 -
 Trumps Pursuit Of Cheap Oil A Complex Relationship With The Industry
May 12, 2025
Trumps Pursuit Of Cheap Oil A Complex Relationship With The Industry
May 12, 2025 -
 Wildfire Betting Ethical Concerns And The Los Angeles Fires
May 12, 2025
Wildfire Betting Ethical Concerns And The Los Angeles Fires
May 12, 2025 -
 Gambling On Natural Disasters The La Wildfire Case Study
May 12, 2025
Gambling On Natural Disasters The La Wildfire Case Study
May 12, 2025
