The Hagia Sophia: 1600 Years Of History And Engineering
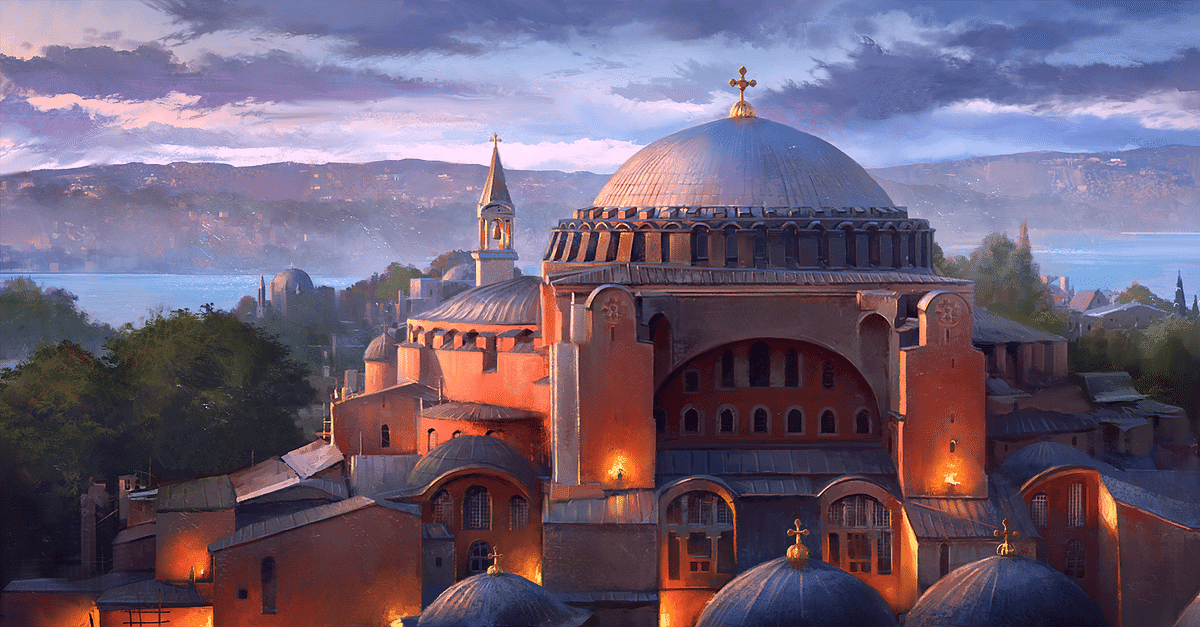

Table of Contents
From Basilica to Mosque to Museum and Back
The Hagia Sophia's history is a captivating journey through time, reflecting the shifting power dynamics and cultural influences of centuries.
The Byzantine Era (532-1453 AD):
Construction of the Hagia Sophia, commissioned by Emperor Justinian I, began in 532 AD. This ambitious project, overseen by architects Anthemius of Tralles and Isidore of Miletus, aimed to create a structure unparalleled in its grandeur and sophistication.
- Architectural Marvels: The Hagia Sophia's most striking feature is its massive dome, a feat of engineering for its time. The use of pendentives—triangular supports—was crucial in allowing the dome to rest on a square base, a groundbreaking innovation. The building also incorporated vast interior spaces, creating a sense of awe and wonder.
- Materials and Techniques: The construction employed brick and mortar, materials skillfully combined to achieve remarkable durability. The use of lightweight materials, such as brick, allowed for the creation of the immense dome. The mortar used was of exceptional quality, enhancing the structure's longevity.
- Religious Significance: The interior mosaics, depicting biblical scenes and figures, were integral to the Hagia Sophia's role as a major center of Byzantine religious life. However, the period of iconoclasm saw many of these images destroyed or covered, reflecting the complex relationship between religion and politics. The impact of iconoclasm is still visible today in the surviving mosaics and the traces of covered images.
The Ottoman Era (1453-1935 AD):
Following the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople in 1453, the Hagia Sophia was converted into a mosque. This transformation marked a new chapter in the building's history, reflecting the cultural and religious dominance of the Ottoman Empire.
- Ottoman Modifications: The addition of four minarets, slender towers from which the call to prayer (adhan) is made, and a mihrab, an alcove indicating the direction of Mecca, signified its new purpose. Extensive calligraphy, an integral part of Islamic art, adorned the interior walls.
- Interior Decorations: The Ottoman period saw the addition of rich carpets, intricate tilework, and stunning calligraphy, creating a visually striking atmosphere that blended Byzantine heritage with Ottoman aesthetics. These additions complemented the existing Byzantine features.
- Cultural Significance: The Hagia Sophia served as a major mosque for centuries, playing a pivotal role in the religious and social life of the Ottoman Empire. Mehmet II, the conqueror of Constantinople, played a crucial part in this transition and the ongoing preservation of the structure.
The Modern Era (1935-Present):
In 1935, under the secular Republic of Turkey's founder, Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, the Hagia Sophia was transformed into a museum. This decision reflected a broader secularizing trend in the nation, yet it also preserved the architectural marvel for all to admire. However, this secular status was recently challenged.
- Museum and Restoration: As a museum, the Hagia Sophia attracted millions of visitors annually, showcasing its historical and architectural significance on a global stage. Significant restoration efforts were undertaken to preserve the structure for future generations, balancing preservation of the historical architecture with conservation of the various additions over the centuries.
- Reclassification as a Mosque: The recent reclassification of the Hagia Sophia as a mosque, a decision that sparked international debate and controversy, highlights the ongoing tension between secularism and religious identity. The change in status demonstrates its enduring importance to the cultural and religious landscape of modern Turkey, and indeed the wider world.
- International Significance: The decision has had a wide-ranging international impact and raised complex questions about heritage preservation, religious freedom, and the interaction between secular and religious identities in a globalized world. This remains a subject of ongoing discussion and analysis.
The Architectural and Engineering Marvels of the Hagia Sophia
The Hagia Sophia's enduring appeal lies not only in its rich history but also in its remarkable architectural and engineering achievements.
The Dome and Pendentives:
The immense dome, measuring approximately 107 feet in diameter, is a testament to the ingenuity of Byzantine engineers. The pendentives, curving triangular sections of masonry, played a vital role in transferring the weight of the dome to the four supporting piers. This elegant solution allowed for the creation of a large, open interior space.
- Architectural Principles: The dome's construction involved sophisticated calculations and meticulous craftsmanship to ensure stability. The precise arrangement of the bricks and mortar optimized weight distribution.
- Materials and Properties: The choice of brick, a relatively lightweight material, was critical in facilitating the construction of such a vast dome. The durability of both brick and the mortar used have contributed to its long-lasting resilience.
- Comparison to Other Structures: The Hagia Sophia's dome was significantly larger and more ambitious than anything previously constructed, influencing subsequent dome designs for centuries.
Structural Innovations:
Beyond the dome, other innovative features contributed to the Hagia Sophia's structural integrity and aesthetic impact.
- Massive Supporting Piers: The use of large, sturdy piers provided a robust foundation for the dome and the overall structure. These piers were designed to efficiently distribute the significant weight of the edifice.
- Brickwork Techniques: The sophisticated bricklaying techniques employed by the Byzantine builders ensured the structural soundness of the massive building. The quality of the brickwork itself is a testament to the skills of those who constructed it.
- Creating Vast Interior Space: Innovative methods were utilized to create a sense of openness and grandeur, maximizing the volume of the interior while minimizing the feeling of enclosure. This innovative approach influenced countless buildings across continents and centuries.
Impact on Later Architecture:
The Hagia Sophia's influence on subsequent architectural styles and structures is undeniable. Its innovative design elements and engineering solutions served as inspiration for countless buildings across various cultures.
- Examples of Influence: The Hagia Sophia's dome, in particular, influenced the design of numerous mosques, cathedrals, and other grand structures across Europe, the Middle East, and beyond. The architectural language of the Hagia Sophia can be seen reverberating through buildings constructed over several centuries and across diverse regions.
- Geographic and Cultural Spread: The design principles and engineering innovations employed in the Hagia Sophia were not confined to a single region; rather, they inspired architects in widely separated locations and within different cultural contexts. This influence highlights the architectural universality of the Hagia Sophia's innovations.
- Lasting Legacy: The Hagia Sophia's impact on architectural history is immeasurable. It continues to serve as a benchmark of architectural excellence and inspires awe in those who have seen it and those who study its design.
Conclusion
The Hagia Sophia's 1600-year journey represents a remarkable blend of history and engineering. From its origins as a magnificent Byzantine basilica to its current status, this iconic structure continues to captivate and inspire. Its architectural innovations, particularly its groundbreaking dome and the use of pendentives, have left an indelible mark on the history of architecture. Learn more about the Hagia Sophia and its enduring legacy – delve deeper into its rich history and marvel at its breathtaking architecture! Consider exploring virtual tours, researching its rich history, or, if possible, experience the wonder of the Hagia Sophia firsthand.

Featured Posts
-
 Louisville Mail Delays End In Sight Says Postal Union
Apr 29, 2025
Louisville Mail Delays End In Sight Says Postal Union
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Relatable Jeff Goldblums Viral Oscar Photo Check
Apr 29, 2025
Relatable Jeff Goldblums Viral Oscar Photo Check
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Jan 6th Hearing Witness Cassidy Hutchinson Announces Memoir
Apr 29, 2025
Jan 6th Hearing Witness Cassidy Hutchinson Announces Memoir
Apr 29, 2025 -
 University Presidents Form Secret Collective To Resist Trump
Apr 29, 2025
University Presidents Form Secret Collective To Resist Trump
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Saudi Arabias Pif Bans Pw C From Advisory Roles For A Year
Apr 29, 2025
Saudi Arabias Pif Bans Pw C From Advisory Roles For A Year
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Closure Of Anchor Brewing Company A Look Back At Its Legacy
May 12, 2025
The Closure Of Anchor Brewing Company A Look Back At Its Legacy
May 12, 2025 -
 Canada Us Tariffs A Partial Removal Predicted
May 12, 2025
Canada Us Tariffs A Partial Removal Predicted
May 12, 2025 -
 The Ftc Investigates Open Ai Understanding The Concerns
May 12, 2025
The Ftc Investigates Open Ai Understanding The Concerns
May 12, 2025 -
 Edan Alexander Hostage Situation Hamas Announces Release
May 12, 2025
Edan Alexander Hostage Situation Hamas Announces Release
May 12, 2025 -
 Us Ambassador Hints At Continued Canadian Tariffs
May 12, 2025
Us Ambassador Hints At Continued Canadian Tariffs
May 12, 2025
