Clean Energy Under Siege: Threats To A Booming Industry

Table of Contents
Political and Regulatory Uncertainty
The clean energy sector is highly sensitive to political and regulatory shifts. Government policies, both supportive and obstructive, significantly influence investment decisions and project viability. This creates a volatile environment, hindering long-term planning and investment certainty.
Shifting Government Policies
Changes in government administrations often lead to shifts in energy priorities. This can result in policies that directly or indirectly undermine the growth of renewable energy.
- Tax breaks for fossil fuels: Subsidies for fossil fuel industries often create an uneven playing field, making renewable energy less competitive.
- Deregulation of emissions standards: Relaxing environmental regulations can reduce the incentive for companies to invest in cleaner energy sources.
- Withdrawal from international climate agreements: This can lead to reduced international cooperation and funding for clean energy projects.
These policy changes impact project financing, investor confidence, and long-term planning. The uncertainty discourages long-term investments, ultimately slowing the transition to a sustainable energy system.
Permitting and Regulatory Delays
Navigating the permitting and approval processes for clean energy projects is often a lengthy and complex undertaking.
- Bureaucratic hurdles: Excessive paperwork, complicated regulations, and multiple agency approvals can significantly delay project timelines.
- Lengthy review processes: Environmental impact assessments and public consultations can take years, adding to the overall project cost.
- Community opposition: Concerns about land use, visual impact, and potential environmental consequences can lead to delays or even project cancellations.
These delays have significant financial and time costs. The longer a project takes to materialize, the higher the risk of cost overruns and the potential for the project to become economically unviable.
Economic Headwinds and Market Volatility
The economic landscape presents further challenges to the clean energy sector. Fluctuating energy prices and supply chain disruptions create uncertainty and hinder investment.
Fluctuating Energy Prices
The price volatility of fossil fuels creates a competitive challenge for renewable energy sources.
- Subsidies for fossil fuels: Continued subsidies for fossil fuels artificially lower their price, making them more competitive compared to unsubsidized renewable energy.
- Global energy market fluctuations: Geopolitical events and unexpected supply shocks can significantly impact energy prices, making renewable energy's long-term price stability less attractive in the short term.
- Effect on renewable energy investment: Price uncertainty makes it difficult for investors to accurately assess the long-term profitability of renewable energy projects.
This price volatility creates significant uncertainty for investors and developers, often leading to project delays or cancellations.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Global supply chain issues significantly impact the availability and cost of raw materials and components necessary for clean energy technologies.
- Material shortages: Shortages of critical raw materials, such as rare earth minerals for wind turbines and solar panels, can delay manufacturing and increase costs.
- Transportation bottlenecks: Disruptions to global shipping and logistics can further exacerbate material shortages and increase costs.
- Geopolitical instability: Political instability in regions with significant resources for clean energy technologies can disrupt supply chains and create price volatility.
These disruptions directly affect manufacturing, project timelines, and the overall cost of clean energy technologies, limiting their affordability and accessibility.
Technological Challenges and Innovation Gaps
Despite significant advancements, technological limitations continue to pose challenges to the widespread adoption of clean energy.
Energy Storage Limitations
One major hurdle is the limitation of current energy storage technologies. The intermittent nature of renewable energy sources like solar and wind requires efficient and reliable energy storage.
- Need for improved battery technology: Developing more efficient, affordable, and longer-lasting batteries is crucial for grid-scale energy storage.
- Pumped hydro storage: While a proven technology, pumped hydro storage is geographically limited and can have significant environmental impacts.
- Other innovative solutions: Research and development into advanced energy storage solutions, such as compressed air energy storage and thermal energy storage, are crucial.
Inadequate storage capacity affects grid stability and the intermittency of renewable energy sources, hindering their widespread adoption.
Grid Infrastructure Constraints
Integrating large amounts of renewable energy into the existing electricity grid requires significant upgrades and expansion.
- Grid modernization: Investing in modernizing the grid infrastructure is essential to handle the fluctuating power output of renewable energy sources.
- Smart grids: Implementing smart grid technologies can improve grid efficiency, reliability, and integration of distributed generation.
- Challenges of integrating distributed generation: Connecting numerous small-scale renewable energy sources to the grid presents significant technical and logistical challenges.
Grid limitations can hinder the growth of clean energy and lead to transmission bottlenecks and power outages.
Conclusion
Clean energy is under siege from multiple fronts. Political uncertainty, economic headwinds, and technological limitations pose significant challenges to the sector's growth and its potential to address climate change. Understanding these threats is crucial to developing effective strategies for overcoming them. The future of clean energy requires addressing policy instability, mitigating economic risks, and accelerating technological innovation. Let's work together to overcome these threats and ensure a sustainable energy future. Learn more about supporting clean energy initiatives in your community today!

Featured Posts
-
 Abn Amro Ziet Occasionverkoop Explosief Groeien Meer Autobezitters Dan Ooit
May 21, 2025
Abn Amro Ziet Occasionverkoop Explosief Groeien Meer Autobezitters Dan Ooit
May 21, 2025 -
 New Attempt To Break The Trans Australia Running World Record
May 21, 2025
New Attempt To Break The Trans Australia Running World Record
May 21, 2025 -
 Los Angeles Wildfires A Reflection Of Societal Shifts And Gambling Trends
May 21, 2025
Los Angeles Wildfires A Reflection Of Societal Shifts And Gambling Trends
May 21, 2025 -
 High Ranking Admirals Fall From Grace Corruption Case Analysis
May 21, 2025
High Ranking Admirals Fall From Grace Corruption Case Analysis
May 21, 2025 -
 The Reality Of Reshoring Manufacturing Jobs To America
May 21, 2025
The Reality Of Reshoring Manufacturing Jobs To America
May 21, 2025
Latest Posts
-
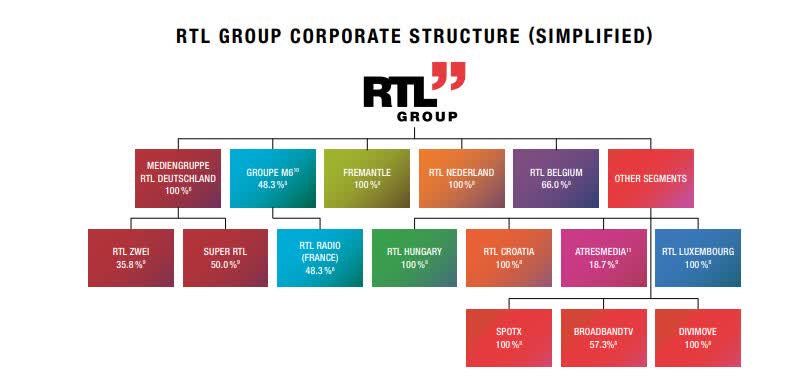 Is Rtl Group Poised For Streaming Success A Look At Profitability Projections
May 21, 2025
Is Rtl Group Poised For Streaming Success A Look At Profitability Projections
May 21, 2025 -
 Architektin Legt Endgueltige Form Am Bau Fest
May 21, 2025
Architektin Legt Endgueltige Form Am Bau Fest
May 21, 2025 -
 Rtl Group Achieving Streaming Profitability Analysis And Outlook
May 21, 2025
Rtl Group Achieving Streaming Profitability Analysis And Outlook
May 21, 2025 -
 Is Mainzs Henriksen The Next Big Managerial Talent After Klopp And Tuchel
May 21, 2025
Is Mainzs Henriksen The Next Big Managerial Talent After Klopp And Tuchel
May 21, 2025 -
 Kaellmanin Ja Hoskosen Sopimus Puolan Seuran Kanssa Paeaettyy
May 21, 2025
Kaellmanin Ja Hoskosen Sopimus Puolan Seuran Kanssa Paeaettyy
May 21, 2025
