Creatine: Benefits, Side Effects, And How To Use It

Table of Contents
The Benefits of Creatine Supplementation
Creatine supplementation offers a wide array of benefits for athletes and fitness enthusiasts alike. Its positive effects on muscle growth, strength, and even cognitive function have made it one of the most popular sports supplements worldwide.
Increased Muscle Strength and Power
Creatine supplementation leads to significant gains in strength and power output, particularly during high-intensity activities. This is because creatine increases the availability of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy source for muscle contractions.
- Improved performance in weightlifting, sprinting, and other anaerobic exercises: Numerous studies demonstrate creatine's effectiveness in enhancing performance in short bursts of intense activity.
- Enhanced muscle phosphocreatine stores, leading to faster ATP regeneration: Creatine helps replenish ATP faster, allowing for more repetitions and improved power output during workouts.
- Studies show creatine improves both short-term and long-term strength gains: The benefits aren't limited to immediate results; consistent creatine use contributes to sustained strength increases over time.
Enhanced Muscle Growth and Hypertrophy
Beyond strength gains, creatine also plays a crucial role in muscle growth and hypertrophy (muscle cell enlargement).
- Creatine promotes muscle protein synthesis: This process is essential for building new muscle tissue.
- Water retention in muscle cells creates a "fuller" look and aids in muscle growth: While some associate water retention with unwanted weight gain, in the context of muscle cells, it contributes to a more defined and larger appearance.
- Creatine supplementation aids in muscle recovery and reduces muscle breakdown: By facilitating faster ATP regeneration, creatine helps reduce muscle soreness and speeds up the recovery process after intense training.
- Synergistic effects when combined with resistance training programs: Creatine's benefits are amplified when combined with a consistent resistance training regimen.
Improved Cognitive Function
While primarily known for its effects on muscle performance, some research suggests that creatine may also offer cognitive benefits.
- Some studies suggest creatine may enhance cognitive functions such as memory and reasoning: This is particularly relevant for individuals engaged in mentally demanding activities.
- May be beneficial for individuals with neurological conditions: Further research is ongoing to explore creatine's potential therapeutic uses in neurological disorders.
- Potential benefits for brain health and neuroprotection: Creatine's ability to boost energy production in the brain may contribute to overall brain health and protection against neurodegenerative diseases.
- Further research is needed to fully understand the cognitive benefits of creatine: While promising, more studies are required to solidify the link between creatine and cognitive enhancement.
Potential Side Effects of Creatine
While generally considered safe, creatine supplementation can lead to some minor side effects in certain individuals.
Water Retention and Weight Gain
One of the most common side effects of creatine is water retention, leading to a temporary increase in body weight.
- Creatine causes water retention, leading to short-term weight gain (mostly water weight): This is primarily due to creatine's effect on muscle cell hydration.
- This is generally considered a harmless side effect: The weight gain is typically temporary and resolves once supplementation ceases.
- Managing water intake can help mitigate this effect: Staying well-hydrated throughout the day can help regulate water retention.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Some individuals experience mild gastrointestinal discomfort when starting creatine supplementation.
- Some individuals experience mild gastrointestinal upset, such as bloating, cramping, or diarrhea, particularly with high doses: These symptoms are usually transient and resolve with continued use.
- Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing can help reduce this: A gradual introduction to creatine allows your body to adapt more easily.
- Proper hydration is crucial to minimize GI discomfort: Adequate fluid intake aids in digestion and reduces the likelihood of gastrointestinal issues.
Rare Side Effects
While less frequent, some rare side effects have been reported.
- Muscle cramps and kidney issues are rare, but potential side effects: These are typically linked to high doses or pre-existing health conditions.
- These are typically associated with misuse and high doses: Adhering to recommended dosages is vital for minimizing the risk of adverse effects.
- Individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions should consult a doctor before using creatine: It's crucial to discuss creatine supplementation with a healthcare professional if you have any underlying health concerns.
How to Use Creatine Effectively
To maximize the benefits of creatine and minimize the risk of side effects, follow these guidelines.
Choosing the Right Creatine
Creatine monohydrate is the most widely researched and effective form of creatine available.
- Creatine monohydrate is the most researched and effective form: Numerous studies support its efficacy and safety.
- Other forms exist (creatine hydrochloride, creatine ethyl ester), but monohydrate offers the best value: While other forms claim improved absorption, creatine monohydrate remains the gold standard.
- Look for reputable brands with third-party testing to ensure purity: Choose brands that prioritize quality control and have independent testing to verify the product's contents.
Loading Phase vs. Maintenance Phase
There are two common approaches to creatine supplementation: a loading phase and a maintenance phase.
- Loading phase involves consuming higher doses (20 grams per day) for the first 5-7 days: This helps saturate your muscles with creatine more quickly.
- Maintenance phase involves consuming lower doses (3-5 grams per day) to maintain muscle creatine stores: This phase helps maintain the benefits achieved during the loading phase.
- Both phases are effective, but the loading phase provides quicker saturation: The choice depends on individual preferences and timelines.
Creatine and Hydration
Adequate hydration is crucial for creatine absorption and to mitigate potential side effects.
- Adequate hydration is crucial for creatine absorption and to prevent side effects: Creatine draws water into muscle cells, so proper hydration is essential.
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially during and after workouts: Staying hydrated supports optimal muscle function and reduces the risk of cramping.
- Dehydration can exacerbate potential side effects like cramping: Ensure you're consuming enough fluids to support your creatine supplementation.
Combining Creatine with Other Supplements
Creatine can be combined with other supplements to support your fitness goals.
- Creatine can be safely combined with other supplements like protein powder and BCAAs: These combinations can further enhance muscle growth and recovery.
- Consider consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized advice: They can help you create a supplement plan tailored to your specific needs and goals.
Conclusion
Creatine is a safe and effective supplement that can significantly enhance athletic performance, promote muscle growth, and potentially improve cognitive function. While some mild side effects like water retention and gastrointestinal upset may occur, these are generally manageable. By following the guidelines outlined above on how to use creatine effectively and safely, you can maximize its benefits and achieve your fitness goals. Remember to consult your doctor before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions. Start reaping the benefits of creatine today and experience the difference! Don't hesitate to explore the power of creatine monohydrate for optimal results in your fitness journey. Learn more about creatine supplementation and unlock your full potential.

Featured Posts
-
 Californias Budget Crisis The Impact Of Trumps Tariffs
May 16, 2025
Californias Budget Crisis The Impact Of Trumps Tariffs
May 16, 2025 -
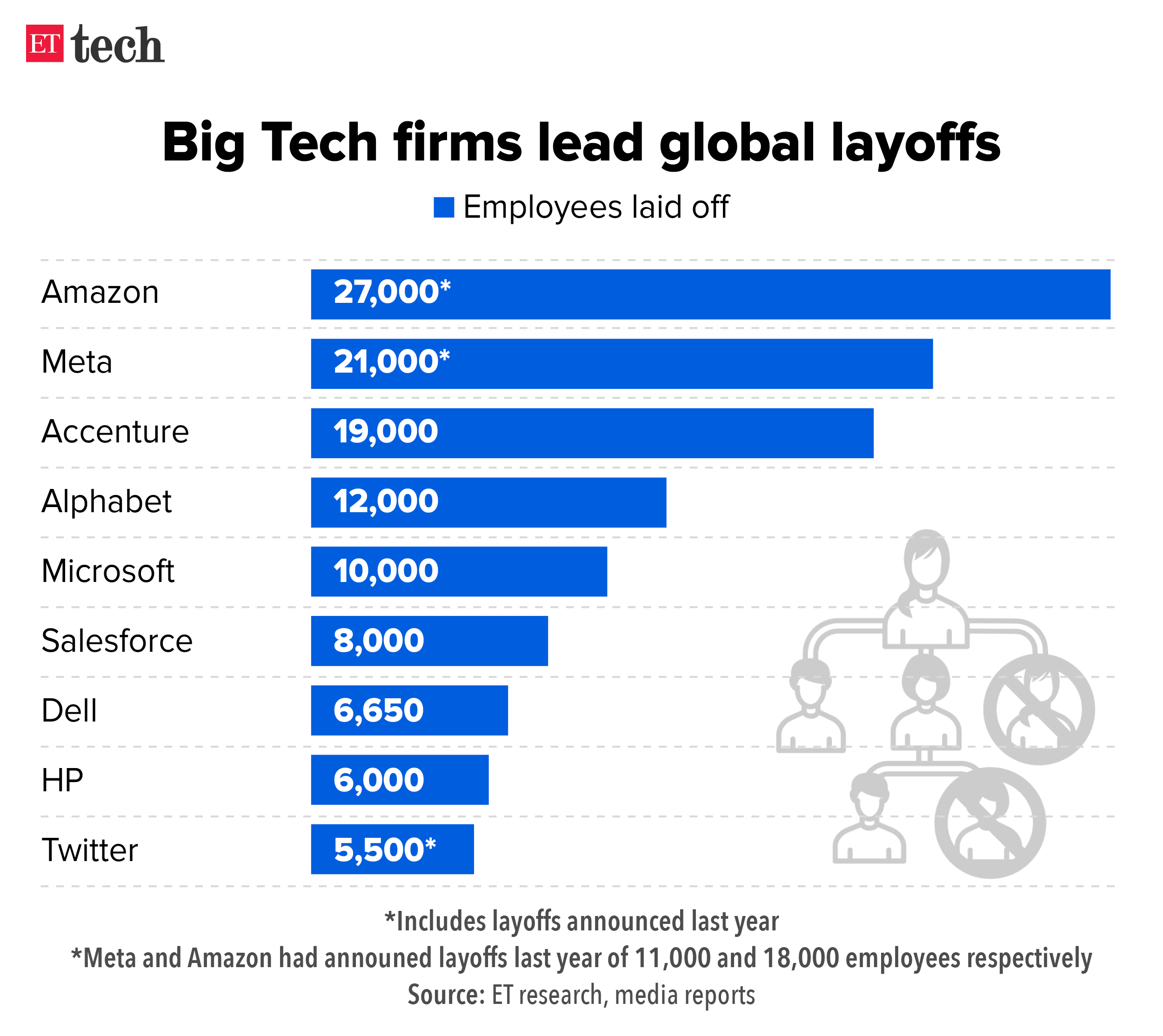 Microsoft Employee Layoffs What We Know So Far
May 16, 2025
Microsoft Employee Layoffs What We Know So Far
May 16, 2025 -
 Los Angeles Dodgers Postseason Performance And Offseason Acquisitions
May 16, 2025
Los Angeles Dodgers Postseason Performance And Offseason Acquisitions
May 16, 2025 -
 Israel Strikes Hamas Leader Mohammed Sinwar In Gaza
May 16, 2025
Israel Strikes Hamas Leader Mohammed Sinwar In Gaza
May 16, 2025 -
 5 Key Dos And Don Ts To Secure A Private Credit Role
May 16, 2025
5 Key Dos And Don Ts To Secure A Private Credit Role
May 16, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Oakland As News Muncys Immediate Impact On The Team
May 16, 2025
Oakland As News Muncys Immediate Impact On The Team
May 16, 2025 -
 Man Convicted For Murder Of Estranged Wifes Friend In Warner Robins
May 16, 2025
Man Convicted For Murder Of Estranged Wifes Friend In Warner Robins
May 16, 2025 -
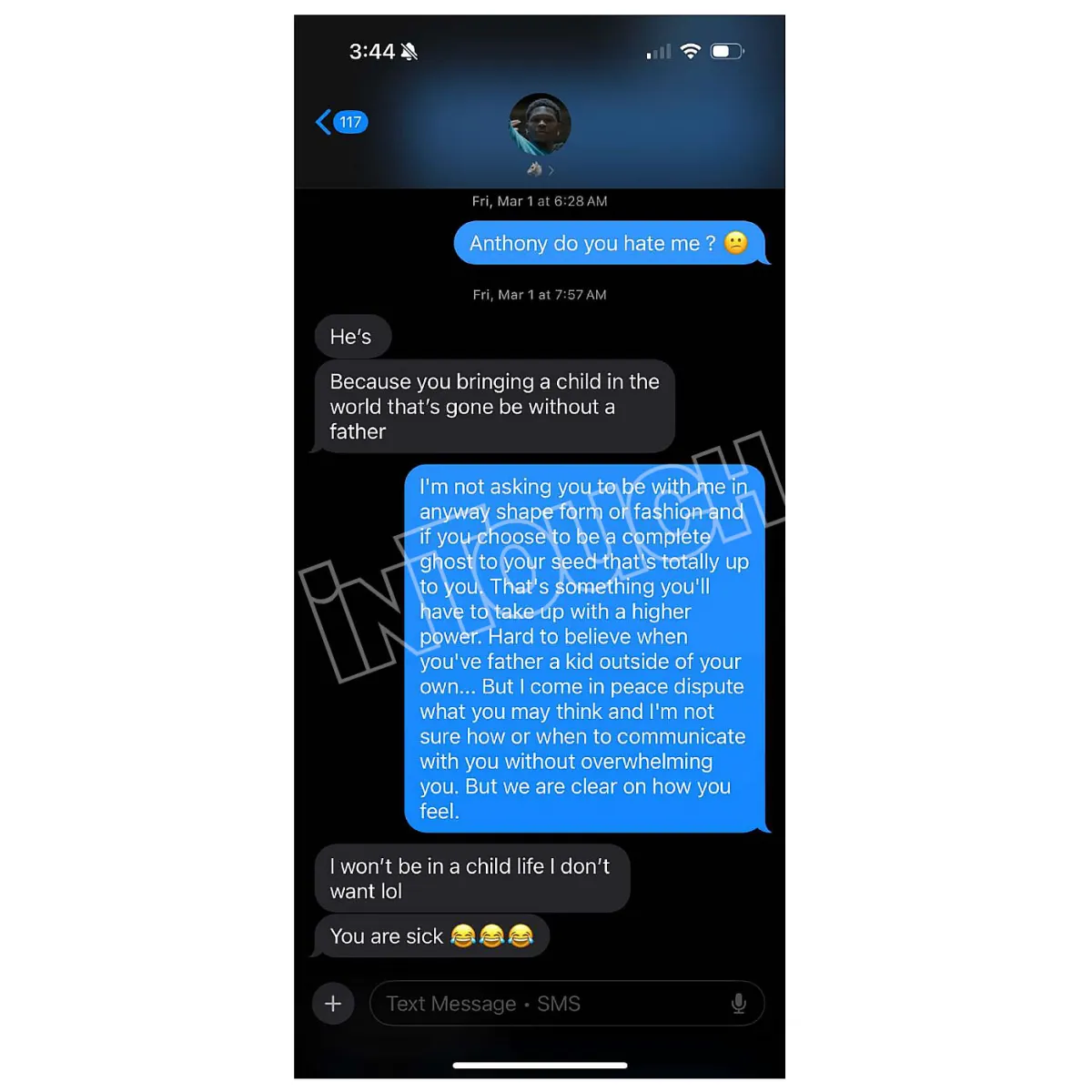 Anthony Edwards Baby Mama Drama The Full Story Unfolds On Twitter
May 16, 2025
Anthony Edwards Baby Mama Drama The Full Story Unfolds On Twitter
May 16, 2025 -
 Oakland As Lineup Change Muncy Starting At Second
May 16, 2025
Oakland As Lineup Change Muncy Starting At Second
May 16, 2025 -
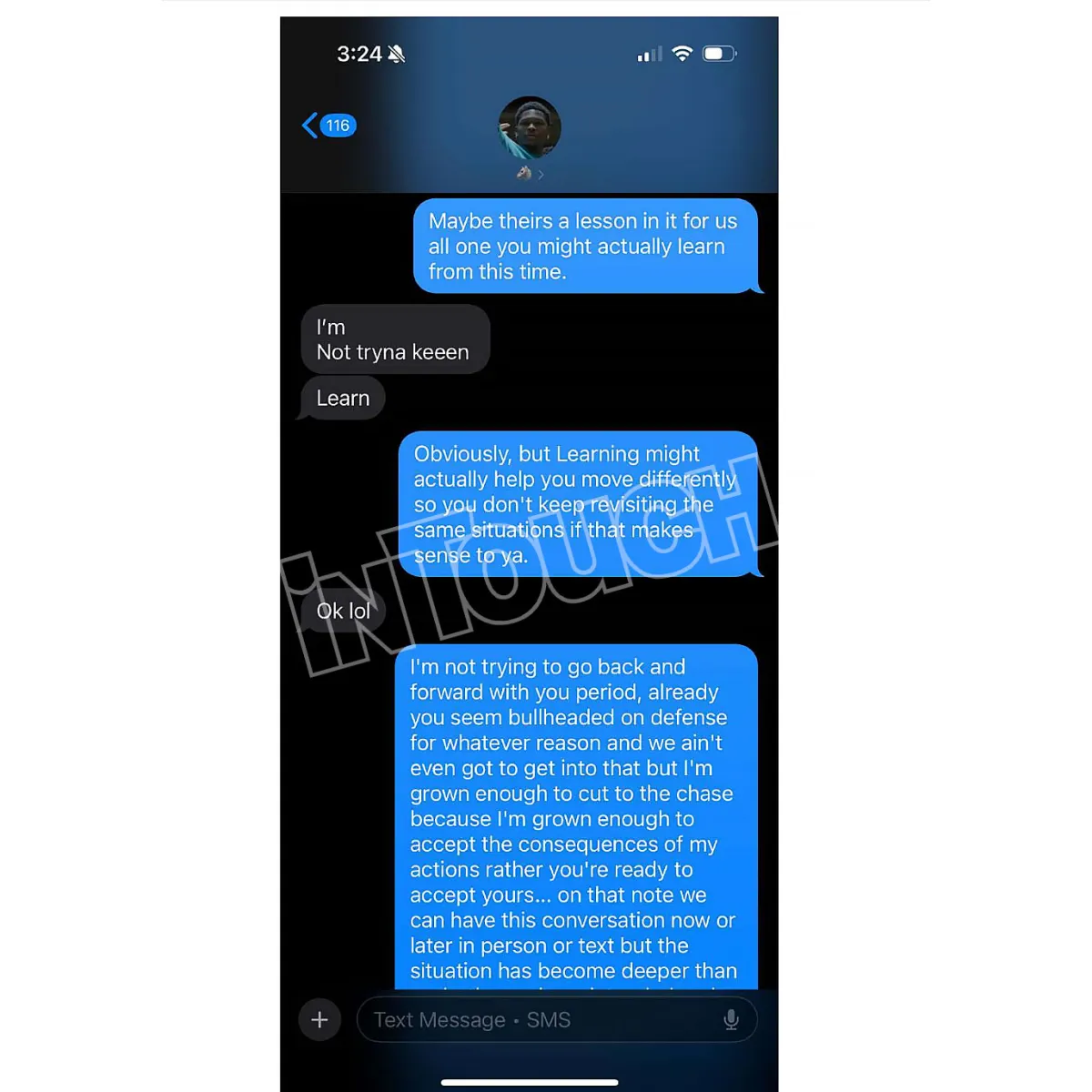 Twitter Explodes Over Anthony Edwards Baby Mama Drama
May 16, 2025
Twitter Explodes Over Anthony Edwards Baby Mama Drama
May 16, 2025
