Kodiak Shellfish Harvest Under Threat: Two Harmful Algal Blooms In A Row
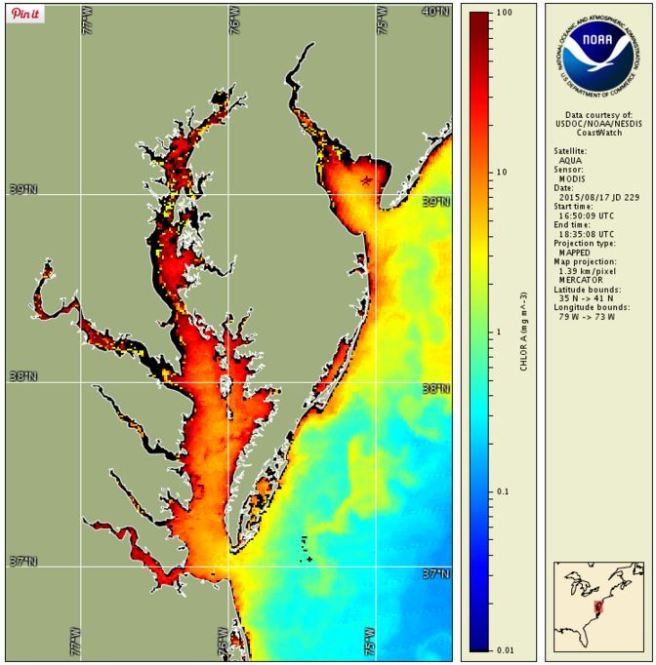
Table of Contents
The Devastating Impact of HABs on Kodiak Shellfish
The proliferation of HABs in Kodiak's waters has far-reaching consequences, impacting both human health and the marine ecosystem.
Shellfish Contamination and Public Health Risks
Harmful algal blooms produce potent toxins that accumulate in shellfish such as clams, mussels, and oysters. When humans consume these contaminated shellfish, they risk serious health consequences. This contamination leads to shellfish harvesting closures, significantly impacting the local economy and food security.
- Specific shellfish affected: Kodiak's commercially important shellfish including butter clams, littleneck clams, and mussels are particularly vulnerable.
- Types of toxins produced: HABs in Kodiak waters can produce toxins causing paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP), amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP), and diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP).
- Symptoms of shellfish poisoning: Symptoms range from tingling and numbness (PSP) to memory loss (ASP) and severe gastrointestinal distress (DSP). Severe cases can be fatal.
- Economic impact: Shellfish harvesting closures due to HABs result in substantial economic losses for fishermen, processors, and related businesses. Tourism reliant on seafood also suffers.
Ecosystem Disruption and Biodiversity Loss
The impact of HABs extends far beyond shellfish contamination. These blooms disrupt the delicate balance of the marine food web, affecting a wide range of species. The toxins produced by HABs can kill fish and other marine life, leading to biodiversity loss and long-term ecosystem damage.
- Affected marine species: Sea otters, seabirds, and other marine mammals that consume contaminated prey are at risk. Even species not directly consuming contaminated shellfish can experience indirect effects.
- Cascading effects: The loss of shellfish and other key species can trigger cascading effects throughout the food web, impacting the entire ecosystem's health and stability.
- Long-term consequences: Repeated HAB events can lead to irreversible damage to the Kodiak ecosystem, potentially impacting the long-term sustainability of the region's fisheries.
- Interconnectedness: Kodiak’s ecosystem is intricately linked. Damage to one component, like shellfish populations, impacts the entire network.
The Causes and Contributing Factors of HABs in Kodiak
Understanding the causes of HABs is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies. While the exact causes are complex and often involve multiple factors, two primary contributors stand out.
Climate Change and its Influence
Climate change plays a significant role in increasing the frequency and intensity of HABs globally, and Kodiak is not immune. Warming ocean temperatures, increased nutrient runoff, and altered ocean currents create favorable conditions for HAB growth.
- Specific climate change data: Data showing rising ocean temperatures in the Gulf of Alaska, increased rainfall and resulting nutrient runoff into coastal waters, and changes in ocean currents impacting nutrient distribution around Kodiak.
- Evidence linking climate change to HABs: Scientific studies showing a correlation between increasing water temperatures and the frequency and intensity of HABs worldwide.
- Predictions for future HAB occurrences: Climate models predict an increased likelihood of more frequent and intense HABs in the future, highlighting the urgent need for action.
Other Contributing Factors
Beyond climate change, other human-induced factors contribute to HABs in Kodiak. These include agricultural runoff containing fertilizers and pesticides, sewage discharge, and the potential impact of aquaculture practices.
- Sources of nutrient pollution: Runoff from agricultural lands and urban areas introduces excess nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) into coastal waters, fueling HAB growth.
- Mitigation strategies: Improved wastewater treatment, sustainable agricultural practices, and responsible land-use planning are crucial for reducing nutrient pollution.
- Areas for future research: Further research is needed to fully understand the relative contributions of different pollution sources to HABs in Kodiak and to refine mitigation strategies.
Mitigation and Conservation Strategies for the Kodiak Shellfish Harvest
Protecting the Kodiak shellfish harvest requires a multifaceted approach combining monitoring, early warning systems, and sustainable management practices.
Monitoring and Early Warning Systems
Early detection of HABs is critical for minimizing their impact. Robust monitoring programs using advanced technologies are essential for providing timely warnings to shellfish harvesters and the public.
- Monitoring techniques: Satellite imagery, water sampling, and toxin analysis are crucial for detecting and quantifying HABs.
- Technologies for early detection: Advanced sensors and automated monitoring systems can improve early warning capabilities.
- Communication strategies: Efficient communication systems are needed to disseminate information quickly to stakeholders and the public.
Sustainable Aquaculture and Fisheries Management
Sustainable aquaculture practices that minimize nutrient pollution and responsible fisheries management are vital for protecting shellfish populations and reducing the risk of HABs.
- Sustainable aquaculture techniques: Implementing best practices for waste management and nutrient control in aquaculture operations can reduce their contribution to HABs.
- Responsible fishing practices: Sustainable fishing quotas and gear restrictions can help maintain healthy shellfish populations.
- Government regulations: Stronger regulations and enforcement are needed to ensure compliance with sustainable aquaculture and fisheries management practices.
Conclusion
The consecutive years of harmful algal blooms pose a significant threat to the Kodiak shellfish harvest, impacting both the ecosystem and the local economy. Understanding the causes of these blooms, implementing effective monitoring systems, and adopting sustainable practices are crucial for protecting this valuable resource. We need immediate and collaborative action to mitigate the effects of HABs and safeguard the future of the Kodiak shellfish harvest. By supporting research, investing in early warning systems, and promoting sustainable practices, we can work together to ensure the long-term health of this vital industry and ecosystem. Let's protect the future of the Kodiak shellfish harvest from further threats of harmful algal blooms and ensure the continued health of this vital resource for future generations.

Featured Posts
-
 Elevated Economic Uncertainty Inflation And Job Losses
May 30, 2025
Elevated Economic Uncertainty Inflation And Job Losses
May 30, 2025 -
 Guillermo Del Toro On Frankenstein Horror Or Something Else A Netflix Movie Review
May 30, 2025
Guillermo Del Toro On Frankenstein Horror Or Something Else A Netflix Movie Review
May 30, 2025 -
 Zayavka Na Uchastie V Otkrytom Seminare Ri Sh V Tolyatti
May 30, 2025
Zayavka Na Uchastie V Otkrytom Seminare Ri Sh V Tolyatti
May 30, 2025 -
 French Open 2024 Swiatek Triumphs As Ruud And Tsitsipas Bow Out
May 30, 2025
French Open 2024 Swiatek Triumphs As Ruud And Tsitsipas Bow Out
May 30, 2025 -
 Undertale 10th Anniversary One Night Only Orchestral Performance
May 30, 2025
Undertale 10th Anniversary One Night Only Orchestral Performance
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Price Caps And Comparison Sites For Vets Under Scrutiny
May 31, 2025
Price Caps And Comparison Sites For Vets Under Scrutiny
May 31, 2025 -
 Rogart Vets Find Temporary Home In Tain Following Devastating Fire
May 31, 2025
Rogart Vets Find Temporary Home In Tain Following Devastating Fire
May 31, 2025 -
 A Plastic Glove Project Fostering Collaboration Between The Rcn And Vet Nursing Professionals
May 31, 2025
A Plastic Glove Project Fostering Collaboration Between The Rcn And Vet Nursing Professionals
May 31, 2025 -
 Watchdog Proposes Price Caps And Vet Comparison Websites
May 31, 2025
Watchdog Proposes Price Caps And Vet Comparison Websites
May 31, 2025 -
 Improving Interprofessional Collaboration Lessons From A Plastic Glove Project Rcn And Vet Nursing
May 31, 2025
Improving Interprofessional Collaboration Lessons From A Plastic Glove Project Rcn And Vet Nursing
May 31, 2025
