More Than BMW And Porsche: Examining The China Problem For Foreign Automakers
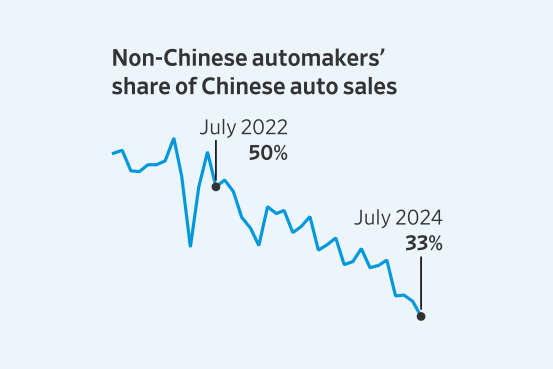
Table of Contents
The Chinese automotive market, the world's largest, is a glittering prize. Yet, beneath the surface of booming sales figures lies a complex web of challenges for foreign automakers. While the struggles of established brands like BMW and Porsche often dominate headlines, the "China Problem" extends far beyond these familiar names, impacting a wide range of international players. This article will delve into the multifaceted issues shaping the fortunes of foreign car companies in China, revealing the nuances of this dynamic and demanding market.
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape
The Chinese automotive regulatory landscape is notoriously intricate, presenting significant hurdles for foreign entrants. These regulations go beyond simple compliance and significantly impact profitability and market access.
- High Import Tariffs: Substantial import tariffs inflate the price of foreign vehicles, making them less competitive against domestically produced alternatives. This directly impacts profitability and necessitates careful pricing strategies.
- Complex Licensing Procedures: Navigating the bureaucratic maze of licensing and approvals can be a time-consuming and expensive process, delaying market entry and increasing operational costs. Foreign companies often require significant local expertise to navigate this complexity.
- Stringent Safety and Emission Standards: China's demanding safety and emission standards necessitate significant investments in research, development, and adaptation of existing models. Failure to meet these standards results in market exclusion.
- Local Content Requirements: Regulations often mandate a certain percentage of locally sourced components, forcing foreign automakers to establish partnerships with Chinese suppliers and integrate into the domestic supply chain. This can be both a challenge and an opportunity, fostering collaboration but also potentially exposing intellectual property.
These regulatory complexities significantly impact the profitability and market entry strategies of foreign automakers, requiring substantial upfront investment and ongoing compliance efforts.
Intense Domestic Competition
The rise of powerful Chinese auto brands represents a formidable challenge to foreign competitors. These domestic players are rapidly gaining market share, leveraging technological advancements and aggressive strategies.
- Technological Advancements: Chinese automakers are making significant strides in electric vehicle (EV) technology, autonomous driving systems, and connected car features, directly competing with, and in some cases surpassing, established international brands.
- Competitive Pricing: Domestic brands often offer aggressively priced vehicles, appealing to price-sensitive consumers and putting pressure on foreign brands to match or differentiate through other value propositions.
- Government Support: Chinese automakers benefit from significant government support, including subsidies, tax breaks, and preferential treatment in areas like licensing and infrastructure development. This provides a substantial competitive advantage.
- Consumer Preference: A growing number of Chinese consumers show a preference for domestically produced vehicles, driven by factors such as patriotism, familiarity with local brands, and the perception of superior after-sales service.
Foreign brands must differentiate themselves through superior technology, brand prestige, unique features, or a compelling customer experience to successfully compete in this increasingly challenging landscape.
Understanding Chinese Consumer Preferences
The Chinese automotive market is not monolithic; understanding the nuances of consumer preferences is crucial for success. Foreign automakers must tailor their offerings and marketing strategies to resonate with specific consumer segments.
- Demand for EVs and NEVs: The Chinese market is a global leader in the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and new energy vehicles (NEVs). Foreign automakers must invest heavily in this segment to remain competitive.
- Brand Prestige and Social Status: For many Chinese consumers, owning a car is a significant social statement. Brand image and perceived prestige play a pivotal role in purchase decisions.
- Digitalization and Connected Car Technology: Chinese consumers are early adopters of advanced technology. Features like in-car entertainment systems, connected services, and autonomous driving capabilities are highly desirable.
- After-Sales Service and Customer Experience: Providing exceptional after-sales service and building strong customer relationships are vital for long-term success in the Chinese market.
Foreign automakers need sophisticated market research and a customer-centric approach to successfully navigate these evolving preferences.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Geopolitical Factors
Operating in China exposes foreign automakers to global supply chain vulnerabilities and geopolitical risks. These factors can significantly impact production, logistics, and overall business continuity.
- Sourcing Challenges: Securing a reliable supply of components and raw materials can be challenging, particularly in times of global supply chain disruptions.
- Trade Tensions and Geopolitical Risks: Escalating trade tensions or unforeseen geopolitical events can significantly impact operations and investment decisions.
- Policy Changes: Unexpected changes in government policy or regulations can create significant uncertainty and operational challenges.
Robust supply chain management, diversification of sourcing, and strategic risk mitigation are essential for foreign automakers operating in China.
Intellectual Property Concerns
Protecting intellectual property (IP) in China remains a significant concern for foreign automakers. The risk of technology theft and counterfeiting necessitates a proactive and comprehensive IP protection strategy.
- Technology Theft and Counterfeiting: The risk of technology theft and the proliferation of counterfeit parts are serious threats, impacting innovation and profitability.
- Enforcement Challenges: Enforcing intellectual property rights in China can be challenging, requiring significant legal resources and expertise.
- Proactive IP Protection: Foreign automakers must adopt proactive strategies to protect their proprietary technologies, including robust legal protection, secure manufacturing processes, and careful management of technology transfer agreements.
These IP concerns significantly impact investment decisions and long-term strategic planning for foreign automakers in China.
Conclusion
The "China Problem" for foreign automakers is not a single issue, but a complex interplay of regulatory hurdles, intense domestic competition, evolving consumer preferences, supply chain vulnerabilities, and intellectual property concerns. Successfully navigating this challenging landscape requires a deep understanding of these multifaceted factors and a well-defined, adaptable strategy. Successfully navigating the complexities of the Chinese automotive market requires a deep understanding of the "China Problem" and a well-defined, adaptable strategy. Learn more about the challenges and opportunities facing foreign automakers in China and develop a winning strategy today.

Featured Posts
-
 Googles Gemini In Chrome A Smaller Step Larger Implications
May 27, 2025
Googles Gemini In Chrome A Smaller Step Larger Implications
May 27, 2025 -
 Avrupa Merkez Bankasi Tarifeler Hakkinda Oenemli Bir Uyari
May 27, 2025
Avrupa Merkez Bankasi Tarifeler Hakkinda Oenemli Bir Uyari
May 27, 2025 -
 Almanacco Del 23 Marzo Compleanni Santo Del Giorno E Proverbio
May 27, 2025
Almanacco Del 23 Marzo Compleanni Santo Del Giorno E Proverbio
May 27, 2025 -
 Apple Tv Studio Show Release Dates Your Guide To Upcoming Episodes
May 27, 2025
Apple Tv Studio Show Release Dates Your Guide To Upcoming Episodes
May 27, 2025 -
 Avrupa Nin Ekonomik Gelecegi Trump Ve Merkez Bankasi Nin Rolue
May 27, 2025
Avrupa Nin Ekonomik Gelecegi Trump Ve Merkez Bankasi Nin Rolue
May 27, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Empanadas De Jamon Y Queso Sin Horno Receta Facil Y Rica
May 31, 2025
Empanadas De Jamon Y Queso Sin Horno Receta Facil Y Rica
May 31, 2025 -
 Deliciosa Sopa Aragonesa Receta Facil Y Rapida Sin Sobres
May 31, 2025
Deliciosa Sopa Aragonesa Receta Facil Y Rapida Sin Sobres
May 31, 2025 -
 El Croque Monsieur Mas Facil Receta Paso A Paso Para Todos
May 31, 2025
El Croque Monsieur Mas Facil Receta Paso A Paso Para Todos
May 31, 2025 -
 Sopa Aragonesa En Menos De 20 Minutos Receta Sencilla
May 31, 2025
Sopa Aragonesa En Menos De 20 Minutos Receta Sencilla
May 31, 2025 -
 Como Hacer Un Croque Monsieur Receta Simple Y Deliciosa Paso A Paso
May 31, 2025
Como Hacer Un Croque Monsieur Receta Simple Y Deliciosa Paso A Paso
May 31, 2025
