Week In Review: Analyzing Failures For Future Success

Table of Contents
Identifying and Defining Failures
Before we can effectively analyze failures, we must clearly identify what constitutes a “failure” in different contexts. The definition of failure can vary greatly depending on whether we're discussing personal goals, professional projects, or business ventures.
-
Differentiate between true failures and minor setbacks: Not every obstacle is a catastrophic failure. A minor setback, such as missing a deadline by a day, is different from failing to launch a product altogether. Effective failure identification requires discerning between these levels of impact.
-
Establish objective criteria for defining failure in your specific situation: What specific metrics define failure in your context? Is it a missed sales target, a failed software launch, or a missed personal deadline? Clearly defined criteria remove ambiguity.
-
Use specific examples to illustrate the difference between a failure and a learning opportunity: A failed experiment in a research setting might provide valuable data, transforming it from a failure into a learning opportunity that informs future research.
-
Avoid emotional biases when identifying failures: Our emotions can cloud our judgment. Objectively assess the situation, separating feelings from facts when defining and analyzing failures. This ensures a more accurate and effective failure identification process.
Effective defining failure involves a clear understanding of the context and the use of objective criteria. Recognizing setbacks as potential learning opportunities allows for a more constructive approach to analyzing failures.
Conducting a Post-Mortem Analysis
A thorough post-mortem analysis is critical for understanding the root causes of a failure. This systematic process allows for a deeper understanding than simply acknowledging the outcome.
-
Employ a structured approach (e.g., 5 Whys analysis): The 5 Whys technique involves repeatedly asking "why" to uncover the root cause of a problem. This helps drill down from the surface-level symptoms to the underlying issues.
-
Gather data from multiple sources (team members, reports, etc.): Don't rely on a single perspective. Collect data from all relevant sources to obtain a comprehensive understanding of the events leading to the failure. This ensures a complete picture for your failure investigation.
-
Identify both immediate and underlying causes of the failure: Often, the immediate cause is a symptom of a deeper, underlying problem. For example, a missed deadline might be due to a lack of resources, which is the underlying cause requiring more attention.
-
Document findings thoroughly for future reference: A well-documented post-mortem analysis becomes a valuable resource for preventing similar failures in the future. This includes detailed descriptions of events, contributing factors, and identified root causes. This structured root cause analysis should become a standard part of your process.
This structured approach to failure investigation will provide the necessary information for a truly effective root cause analysis.
Learning from Failures: Extracting Valuable Lessons
The true value of analyzing failures lies in transforming the analysis into actionable insights. This step translates the findings from the post-mortem into concrete steps to improve.
-
Identify specific areas for improvement: What processes, systems, or individual skills contributed to the failure? Identifying these specific weaknesses is key for future improvements.
-
Develop strategies to mitigate similar failures in the future: Based on the identified areas for improvement, create specific, actionable strategies to prevent similar incidents from occurring again.
-
Implement changes in processes, systems, or behaviors: Put your strategies into action! This might involve revising workflows, updating software, or implementing new training programs.
-
Share learnings with the team to foster a culture of continuous improvement: Openly discuss the lesson learned with the team to promote transparency, learning, and collective growth. This supports a culture of continuous learning and adaptation.
This process of extracting lesson learned from failure analysis is vital to achieving continuous improvement and future success.
Preventing Future Failures: Implementing Preventative Measures
The final, and perhaps most important, step is implementing preventative measures to avoid repeating past mistakes.
-
Develop and implement new processes or procedures: Based on your analysis, revise existing procedures or create new ones that address the identified shortcomings. This is a core component of failure prevention.
-
Improve communication and collaboration within the team: Poor communication can lead to costly failures. Enhance communication channels and collaboration practices to prevent future issues.
-
Invest in training and development to address skill gaps: If skill deficiencies contributed to the failure, invest in training programs to upskill your team.
-
Establish a system for tracking and monitoring progress: Implement a system to track progress and measure the effectiveness of the implemented preventative measures. This proactive risk management approach is crucial to ensure continued success.
Through implementing these preventative measures, you'll effectively reduce the likelihood of similar failures. Strong process improvement driven by effective failure analysis forms the basis for robust risk management.
Conclusion
Regularly analyzing failures is not about dwelling on mistakes, but about using them as stepping stones to future success. By systematically identifying, analyzing, and learning from setbacks, we can significantly improve our performance, build resilience, and achieve better outcomes. The process of failure analysis should be integrated into our regular routines to ensure continuous improvement.
Start analyzing failures today! Take the time to reflect on recent setbacks, identify the root causes, and develop strategies to prevent similar failures in the future. By embracing a proactive approach to failure analysis, you'll unlock significant potential for growth and achievement. Remember, every failure is an opportunity to learn and improve – don’t let them go to waste.

Featured Posts
-
 Mariners Giants Injury News Key Players Out April 4 6
May 17, 2025
Mariners Giants Injury News Key Players Out April 4 6
May 17, 2025 -
 Should I Refinance My Federal Student Loans A Step By Step Analysis
May 17, 2025
Should I Refinance My Federal Student Loans A Step By Step Analysis
May 17, 2025 -
 Jim Morrison Sighting New York Maintenance Man Claim
May 17, 2025
Jim Morrison Sighting New York Maintenance Man Claim
May 17, 2025 -
 Is Jim Morrison Still Alive A New York Maintenance Man Theory
May 17, 2025
Is Jim Morrison Still Alive A New York Maintenance Man Theory
May 17, 2025 -
 Trump Tariffs And The Price Of Phone Repairs A Consumers Dilemma
May 17, 2025
Trump Tariffs And The Price Of Phone Repairs A Consumers Dilemma
May 17, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Principal Financial Group Nasdaq Pfg 13 Analyst Opinions And What They Mean
May 17, 2025
Principal Financial Group Nasdaq Pfg 13 Analyst Opinions And What They Mean
May 17, 2025 -
 1 4 112
May 17, 2025
1 4 112
May 17, 2025 -
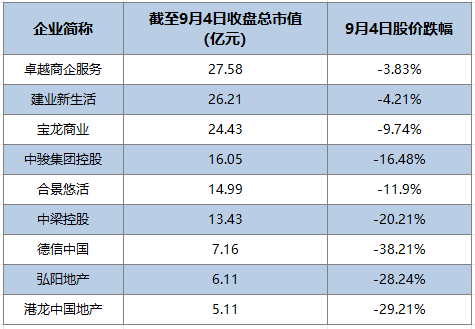 112
May 17, 2025
112
May 17, 2025 -
 13 Analyst Assessments Of Principal Financial Group Pfg Key Insights For Investors
May 17, 2025
13 Analyst Assessments Of Principal Financial Group Pfg Key Insights For Investors
May 17, 2025 -
 Delay Of 2024 Financial Report Publication An Update From Valerio Therapeutics S A
May 17, 2025
Delay Of 2024 Financial Report Publication An Update From Valerio Therapeutics S A
May 17, 2025
