Analysis: Japan's Steep Bond Curve And Its Economic Impact
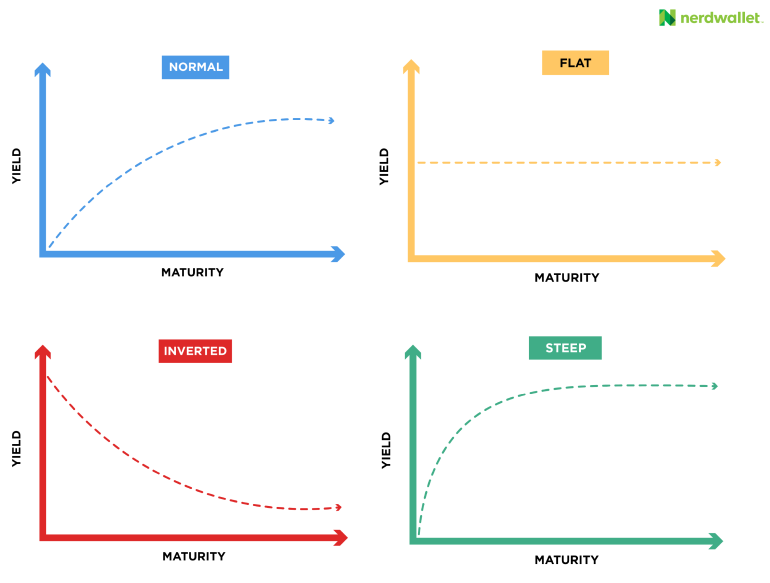
Table of Contents
Factors Contributing to Japan's Steep Bond Curve
Several intertwined factors contribute to the unusual shape of Japan's yield curve. Understanding these elements is crucial to grasping the broader economic implications.
The Role of the Bank of Japan (BOJ)'s Yield Curve Control (YCC) Policy
The Bank of Japan's Yield Curve Control (YCC) policy is a cornerstone of its monetary strategy. YCC aims to manage the yield on 10-year Japanese Government Bonds (JGBs), effectively setting an upper limit. This policy has artificially suppressed short-term interest rates, keeping them exceptionally low. Simultaneously, longer-term yields, while influenced by the BOJ's actions, have remained relatively higher, leading to the steep curve.
- Artificial suppression of short-term yields: The BOJ's massive asset purchases under YCC have kept short-term JGB yields near zero.
- Limited effectiveness in stimulating inflation: Despite the low short-term rates, inflation in Japan has remained stubbornly low, failing to reach the BOJ's target.
- Market distortions caused by the intervention: The BOJ's interventions have created distortions in the bond market, making it difficult to gauge true market sentiment and expectations.
Inflationary Pressures and Market Expectations
While Japan's inflation remains relatively muted compared to other developed nations, inflationary pressures are emerging. Rising import costs due to a weaker yen and global commodity price increases are putting upward pressure on prices. However, wage growth has lagged, limiting the inflationary impact. Despite the relatively low inflation, market participants anticipate future interest rate hikes, both domestically and globally, contributing to higher longer-term yields on JGBs.
- Rising import costs: The weakening yen has increased the cost of imported goods, fueling inflationary pressures.
- Wage growth (or lack thereof): The absence of significant wage growth dampens inflationary pressures despite rising import costs.
- Market speculation regarding BOJ policy changes: Market speculation about the BOJ potentially abandoning or adjusting its YCC policy contributes to uncertainty and influences longer-term bond yields.
Global Economic Factors and Capital Flows
Global economic factors, particularly the actions of the US Federal Reserve, significantly influence Japan's bond market. The Fed's interest rate hikes draw capital away from Japan, potentially putting upward pressure on longer-term JGB yields. However, Japan's JGBs still retain their safe-haven status, attracting investors seeking stability amidst global uncertainty. Foreign investor sentiment, therefore, plays a crucial role in shaping the bond curve.
- Impact of US Federal Reserve policy: The Fed's monetary tightening policies directly impact global capital flows, affecting JGB yields.
- Safe-haven status of JGBs: JGBs remain a haven for investors seeking safety during times of global economic uncertainty.
- Foreign investor sentiment towards Japan: Shifting investor confidence in the Japanese economy influences demand for JGBs, impacting yields.
Economic Implications of Japan's Steep Bond Curve
The steepness of Japan's yield curve carries significant implications for the Japanese economy.
Impact on Economic Growth
A steep yield curve, with higher long-term yields, can increase borrowing costs for businesses and individuals, potentially hindering economic growth. Higher borrowing costs can lead to reduced investment and consumer spending, dampening economic activity.
- Increased borrowing costs for businesses: Higher long-term interest rates make it more expensive for businesses to borrow money for investment.
- Reduced consumer confidence: Rising borrowing costs can also negatively affect consumer confidence and spending.
- Impact on capital expenditure: Higher interest rates may discourage businesses from undertaking capital expenditure projects.
Effects on Inflation
The relationship between a steep yield curve and inflation in Japan is complex. While higher long-term yields could contribute to higher inflation through increased borrowing costs and potentially higher import prices, the BOJ's continued monetary easing efforts complicate this relationship. The BOJ's challenge lies in managing the delicate balance between stimulating growth and controlling inflation.
- Potential for higher inflation due to increased borrowing costs: Higher borrowing costs can filter through to higher prices for goods and services.
- Impact on import prices: Changes in interest rates can influence the value of the yen, affecting import prices.
- BOJ's challenge in managing inflation: The BOJ faces the challenge of achieving its inflation target while managing the economic impact of a steep yield curve.
Challenges for Monetary Policy
The steep yield curve presents significant challenges for the BOJ's monetary policy. Maintaining its YCC policy despite market pressures and balancing economic growth with price stability requires a careful navigation of complex economic forces. The BOJ may need to consider policy adjustments to address the evolving situation.
- Maintaining YCC policy despite market pressures: The BOJ faces pressure to adjust its YCC policy in response to market forces.
- Balancing economic growth and price stability: The BOJ must navigate the trade-off between stimulating economic growth and controlling inflation.
- Potential for policy adjustments: The BOJ may need to make adjustments to its monetary policy in response to the steep yield curve.
Conclusion
Japan's steep bond curve is a product of the BOJ's YCC policy, emerging inflationary pressures, and global economic influences. This unusual shape has significant implications for economic growth, inflation, and the BOJ's ability to manage monetary policy. The increased borrowing costs associated with the steep curve pose a challenge to economic expansion, while the interplay between yield curves, inflation expectations, and BOJ interventions creates a complex environment. Understanding Japan's steep bond curve is crucial for navigating the complexities of the Japanese economy. Continue to follow our analysis for further insights into the evolving dynamics of Japan's bond market and its economic impact.

Featured Posts
-
 Car Dealerships Renew Resistance To Electric Vehicle Mandates
May 17, 2025
Car Dealerships Renew Resistance To Electric Vehicle Mandates
May 17, 2025 -
 High School Confidential 2024 25 Key Events Of Week 26
May 17, 2025
High School Confidential 2024 25 Key Events Of Week 26
May 17, 2025 -
 The Problem Of False Angel Reese Quotes Circulating On Social Media
May 17, 2025
The Problem Of False Angel Reese Quotes Circulating On Social Media
May 17, 2025 -
 Tokyos Quiet Revolution Soundproof Real Estate For A Peaceful Urban Lifestyle
May 17, 2025
Tokyos Quiet Revolution Soundproof Real Estate For A Peaceful Urban Lifestyle
May 17, 2025 -
 New York Knicks How To Handle The Landry Shamet Question
May 17, 2025
New York Knicks How To Handle The Landry Shamet Question
May 17, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Midday Interview Securing The Fountain City Classic Scholarship
May 17, 2025
Midday Interview Securing The Fountain City Classic Scholarship
May 17, 2025 -
 Is Refinancing Federal Student Loans With A Private Lender Right For You
May 17, 2025
Is Refinancing Federal Student Loans With A Private Lender Right For You
May 17, 2025 -
 Would Privatizing Student Loans Under Trump Benefit Or Harm Borrowers
May 17, 2025
Would Privatizing Student Loans Under Trump Benefit Or Harm Borrowers
May 17, 2025 -
 Private Lender Refinancing A Guide To Federal Student Loans
May 17, 2025
Private Lender Refinancing A Guide To Federal Student Loans
May 17, 2025 -
 Governments Increased Enforcement Of Student Loan Repayment A Borrowers Guide
May 17, 2025
Governments Increased Enforcement Of Student Loan Repayment A Borrowers Guide
May 17, 2025
