The Challenges Of Producing All-American Goods

Table of Contents
Rising Production Costs in the United States
Producing All-American goods often comes at a premium. Several factors contribute to significantly higher production costs in the US compared to many overseas competitors.
Labor Costs
American workers are among the highest-paid globally. This significantly impacts the cost of manufacturing.
- Higher minimum wages: The US minimum wage, while varying by state, is considerably higher than in many other manufacturing hubs.
- Comprehensive benefits packages: American companies often provide extensive benefits, including health insurance, paid time off, and retirement plans, adding to labor costs.
- Employee healthcare costs: The cost of providing healthcare to employees is a substantial expense for US businesses, unlike in many countries with national healthcare systems.
These higher labor costs directly affect the price competitiveness of American-made products in the global market. For example, a simple comparison of labor costs in the US versus China reveals a substantial difference, making it difficult for American manufacturers to compete on price alone. This necessitates a focus on higher value-added products and niche markets to remain profitable.
Raw Material Costs
Sourcing raw materials domestically also presents challenges.
- Transportation costs: Moving raw materials across the vast distances of the US can be expensive, particularly with fluctuating fuel prices.
- Potential scarcity of certain materials: The US may lack readily available sources for certain raw materials, necessitating imports which negate some of the benefits of domestic production.
- Stringent environmental regulations: While beneficial for the environment, complying with US environmental regulations adds to the cost of sourcing and processing raw materials.
The volatile nature of energy prices further exacerbates the issue. Higher energy costs translate directly into increased manufacturing expenses, impacting the overall profitability of domestic production.
Regulatory Compliance
Navigating the complex web of US regulations adds another layer of cost to American manufacturing.
- Compliance with EPA standards: Meeting Environmental Protection Agency standards for emissions and waste disposal is crucial but costly.
- FDA regulations (if applicable): Industries producing food, drugs, or medical devices face stringent FDA regulations, adding to compliance costs.
- OSHA regulations: Occupational Safety and Health Administration regulations aim to protect workers but require significant investment in safety measures and training.
The bureaucratic process of obtaining permits and licenses, along with the potential for hefty fines for non-compliance, further increases the burden on domestic producers. These regulatory costs are often significantly lower in many other countries.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Infrastructure Limitations
The reliability of the US supply chain is another significant obstacle for domestic manufacturers.
Dependence on Foreign Suppliers
Many American manufacturers rely on imported components and materials, creating vulnerability.
- Global supply chain disruptions: Events like the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the fragility of global supply chains, causing significant delays and shortages.
- Geopolitical instability: International conflicts and political tensions can disrupt the flow of imported materials, impacting production.
- Trade wars: Tariffs and trade disputes can significantly increase the cost of imported goods and create uncertainty for businesses.
This dependence on foreign suppliers creates risks that domestic-only production strategies can mitigate. However, establishing fully independent supply chains requires significant investment and may not always be feasible.
US Infrastructure Deficiencies
Outdated infrastructure further complicates domestic production.
- Aging roads and bridges: Poor road conditions increase transportation costs and delivery times.
- Port congestion: Overcrowded ports lead to delays in shipping raw materials and finished goods.
- Lack of high-speed rail: The absence of a robust high-speed rail network hinders efficient transportation of goods across long distances.
These infrastructure limitations add significant costs and delays, making American manufacturers less competitive compared to those in countries with more modern infrastructure.
Competition from Overseas Manufacturers
American manufacturers face stiff competition from overseas producers, particularly those in countries with lower labor and production costs.
Lower Labor Costs Abroad
The cost advantage enjoyed by manufacturers in countries with significantly lower labor costs remains a substantial challenge.
- Examples of countries with significantly lower labor costs: Countries like China, Vietnam, and Bangladesh offer significantly lower labor costs, making it difficult for US manufacturers to compete on price.
- Outsourcing trends: Many companies continue to outsource manufacturing to these countries to reduce costs.
This competitive pressure forces American manufacturers to focus on innovation, quality, and specialized products to justify higher prices.
Government Subsidies and Trade Policies
Foreign governments often provide substantial subsidies and favorable trade policies to their domestic industries, further impacting competitiveness.
- Examples of government support for overseas manufacturers: Many countries offer tax breaks, grants, and other incentives to attract and support their manufacturing sectors.
- Tariffs and trade agreements: Trade policies, including tariffs and trade agreements, can create an uneven playing field, favoring certain countries over others.
These policies often make it difficult for American manufacturers to compete fairly in the global marketplace, highlighting the need for policies that support domestic industries.
Conclusion
The challenges of producing All-American goods are multifaceted and significant. High production costs, driven by labor expenses, raw material costs, and regulatory compliance, combine with supply chain vulnerabilities and intense competition from overseas manufacturers to create a complex landscape for domestic producers. While the desire for "Made in the USA" products remains strong, achieving widespread domestic production requires addressing these systemic issues. Discover how you can support the growth of All-American goods and strengthen our national economy by learning more about the initiatives promoting domestic manufacturing and supporting American businesses.

Featured Posts
-
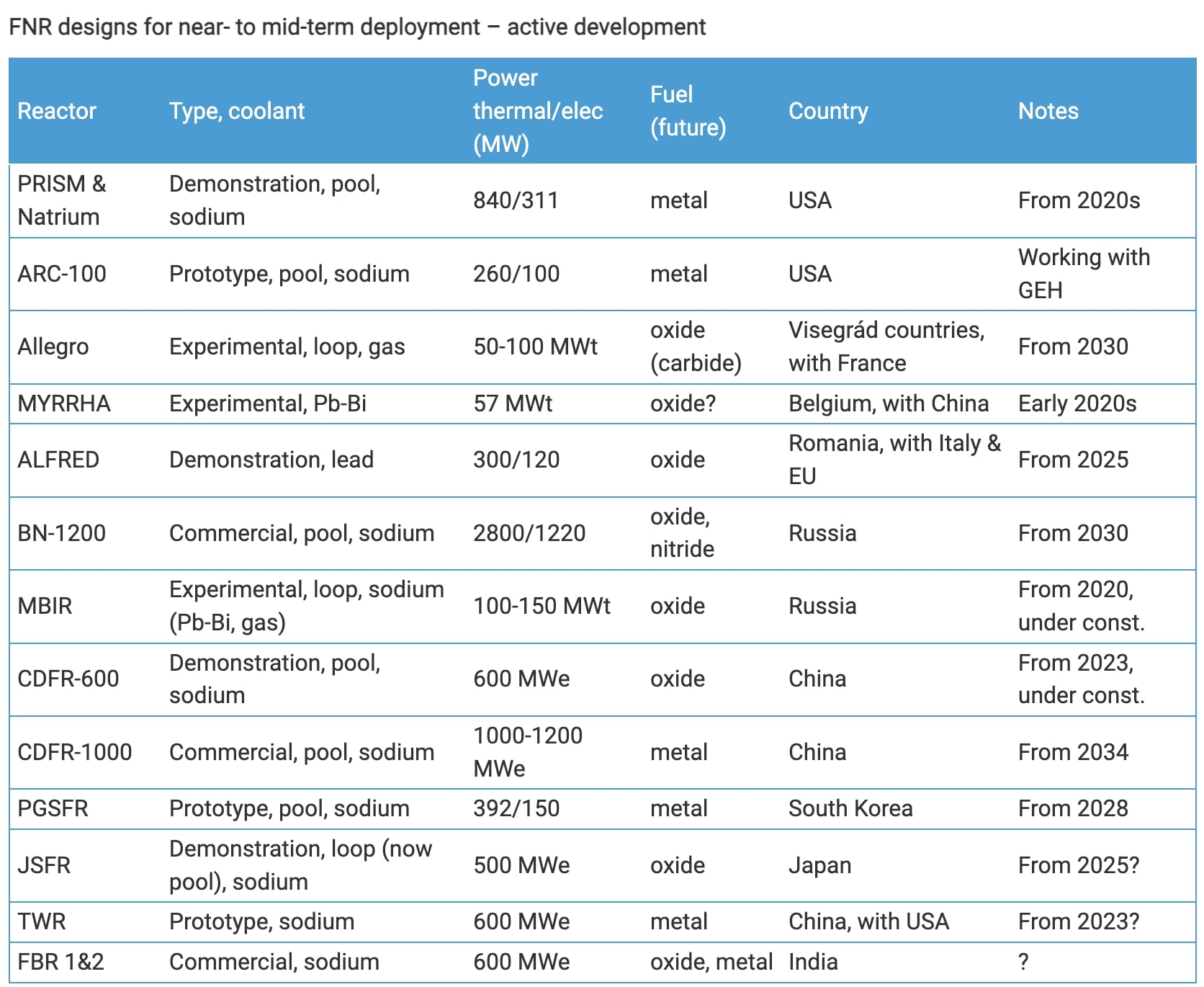 Ten New Nuclear Reactors Approved In Chinas Energy Plan
Apr 29, 2025
Ten New Nuclear Reactors Approved In Chinas Energy Plan
Apr 29, 2025 -
 The Impact Of Over The Counter Birth Control In A Post Roe World
Apr 29, 2025
The Impact Of Over The Counter Birth Control In A Post Roe World
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Trumps Potential Pardon Of Pete Rose A Look At The Mlb Betting Ban
Apr 29, 2025
Trumps Potential Pardon Of Pete Rose A Look At The Mlb Betting Ban
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Cardinal Maintains Entitlement To Vote In Next Papal Election
Apr 29, 2025
Cardinal Maintains Entitlement To Vote In Next Papal Election
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Russias Military Buildup A Growing Threat To European Security
Apr 29, 2025
Russias Military Buildup A Growing Threat To European Security
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 High Stock Valuations Bof As View And Investor Implications
May 12, 2025
High Stock Valuations Bof As View And Investor Implications
May 12, 2025 -
 Bof A On Stock Market Valuations Why Investors Shouldnt Panic
May 12, 2025
Bof A On Stock Market Valuations Why Investors Shouldnt Panic
May 12, 2025 -
 Stock Market Valuations Bof As Reassurance For Investors
May 12, 2025
Stock Market Valuations Bof As Reassurance For Investors
May 12, 2025 -
 Analyzing Trumps Stance On Cheap Oil Implications For The Energy Sector
May 12, 2025
Analyzing Trumps Stance On Cheap Oil Implications For The Energy Sector
May 12, 2025 -
 Trumps Embrace Of Cheap Oil Challenges And Consequences For The Energy Industry
May 12, 2025
Trumps Embrace Of Cheap Oil Challenges And Consequences For The Energy Industry
May 12, 2025
